A Raspberry Pi LCD library for the widely used Hitachi HD44780 controller.
Project description
A Python 2/3 Raspberry PI Character LCD library for the Hitachi HD44780 controller.
Tested with the 20x4 LCD that is sold for example by adafruit.com or mikroshop.ch.
Also tested with a 16x2 LCD from mikroshop.ch.
This library is inspired by Adafruit Industries’ CharLCD library as well as by Arduino’s LiquidCrystal library.
The GPIO access is provided by the great RPIO library.
Features
Simple to use API
Support for both 4 bit and 8 bit modes
Python 2/3 compatible
Caching: Only write characters if they changed
Example
Writing To Display
Basic text output with multiline control.
>>> from RPLCD import CharLCD
>>> lcd = CharLCD()
>>> lcd.write_string('Raspberry Pi HD44780')
>>> lcd.cursor_pos = (2, 0)
>>> lcd.write_string('http://github.com/\n\rdbrgn/RPLCD')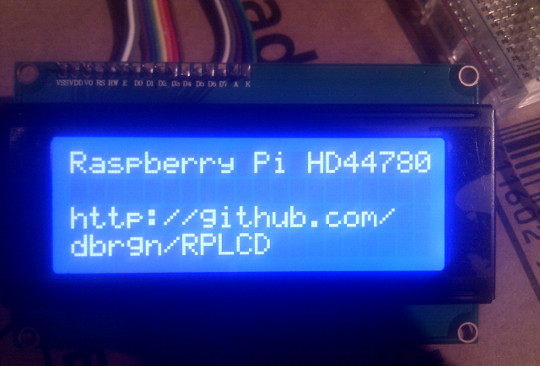
Context Managers
Unlike other uses of context managers, these implementations prepare the configuration before writing to the display, but don’t reset it after the block ends.
>>> from RPLCD import CharLCD, cleared, cursor
>>> lcd = CharLCD()
>>>
>>> with cleared(lcd):
>>> lcd.write_string('LCD is cleared.')
>>>
>>> with cursor(lcd, 2, 0):
>>> lcd.write_string('This is he 3rd line.')Installing
(TLDR: Use pip install RPLCD)
Prerequisites
As prerequisite to build the RPIO dependency, you need the python-dev package. And to install the package itself, you’ll want to use pip. Both should already be installed on a regular Raspbian image. Otherwise, install them:
$ sudo apt-get install python-dev python-pip
Virtualenv Installation
I would recommend you to always use virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper when developing Python applications. This way, you have an isolated environment for each project, which prevents package version conflicts.
To install virtualenv and virtualenvwrapper:
$ sudo apt-get install virtualenvwrapper
Log out and back in to activate the virtualenvwrapper scripts. Then create a new virtualenv:
$ mkvirtualenv myproject
To enable the virtualenv, use workon myproject and to disable it use deactivate.
Then install the RPLCD library with its dependencies:
$ pip install RPLCD
Systemwide Installation
If you want you can also skip the virtualenv part and install the library system-wide. In that case just run pip as root:
$ sudo pip install RPLCD
Manual Installation
You can also install the library manually without pip. Either just copy the scripts to your working directory and import them, or download the repository and run python setup.py install to install it into your Python package directory.
Wiring
The standard wiring configuration uses the following pins (BOARD numbering scheme rev 2):
RS: 15
RW: 18
E: 16
Data 4-7: 21, 22, 23, 24

API
Init, Setup, Teardown
import RPIO
from RPLCD import CharLCD
# Initialize display. All values have default values and are therefore
# optional.
lcd = CharLCD(pin_rs=15, pin_rw=18, pin_e=16, pins_data=[21, 22, 23, 24],
numbering_mode=RPIO.BOARD,
cols=20, rows=4, dotsize=8)
...
# If desired, reset the GPIO configuration and optionally clear the screen.
# Note that this can lead to undesired effects on the LCD, because the GPIO
# pins are not configured as input or output anymore.
lcd.close(clear=True)Properties
display_enabled -> True / False
cursor_pos -> (row, col)
text_align_mode -> Alignment.left / Alignment.right
write_shift_mode -> ShiftMode.cursor / ShiftMode.display
cursor_mode -> CursorMode.hide / CursorMode.line / CursorMode.blink
High Level Functions
write_string(value): Write the specified string to the display. You can use newline (\n) and carriage return (\r) characters.
clear(): Overwrite display with blank characters and reset cursor position.
home(): Set cursor to initial position and reset any shifting.
shift_display(amount): Shift the display. Use negative amounts to shift left and positive amounts to shift right.
Mid Level Functions
write(value): Send a raw command to the LCD.
command(value): Write a raw byte to the LCD.
Context Managers
cursor(lcd, row, col): Control the cursor position before entering the block.
cleared(lcd): Clear the display before entering the block.
Testing
To test your 20x4 display, please run the test_20x4.py script and confirm/verify each step with the enter key. If you don’t use the standard wiring, make sure to add your pin numbers to the CharLCD constructor in test_20x4.py.
To test a 16x2 display, procede as explained above, but use the test_16x2.py script instead.
Resources
TC2004A-01 Data Sheet: http://www.adafruit.com/datasheets/TC2004A-01.pdf
HD44780U Data Sheet: http://www.adafruit.com/datasheets/HD44780.pdf
License
This code is licensed under the MIT license, see the LICENSE file or tldrlegal for more information.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
File details
Details for the file RPLCD-0.1.3.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: RPLCD-0.1.3.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 11.1 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 6a57987d03a2845b1b76c1a851843be22672046e689d542675db30a4971cab68 |
|
| MD5 | e4c43acfab4029f84cd217fad618844b |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 0bc6e95bc45949db0d8627feabdbbc9e6a49ae75d672b40ed44500d40d050e21 |











