M/EEG power regression pipelines in Python
Project description
Covariance Data Frames for Predictive M/EEG Pipelines
Summary
The coffeine library implements provides a high-level interface to the predictive modeling techniques focusing on the M/EEG covariance matrix as representation of the signal. The methods implemented here are built on top of PyRiemann while the API is designed with the more specific use-case of building biomedical prediction models from M/EEG signals. For this purpose, coffeine uses DataFrames to handle multiple covariance matrices alongside scalar features. Vectorization and model composition functions are provided that handle composition of scikit-learn compatible modeling pipelines from covariances alongside other types of features.
For details on the feature extraction pipelines and statistical models, please consider the following references:
[1] D. Sabbagh, P. Ablin, G. Varoquaux, A. Gramfort, and D. A. Engemann. Predictive regression modeling with MEG/EEG: from source power to signals and cognitive states. NeuroImage, page 116893,2020. ISSN 1053-8119. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811920303797
[2] D. Sabbagh, P. Ablin, G. Varoquaux, A. Gramfort, and D. A. Engemann. Manifold-regression to predict from MEG/EEG brain signals without source modeling. NeurIPS (Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems) 32. https://papers.nips.cc/paper/8952-manifold-regression-to-predict-from-megeeg-brain-signals-without-source-modeling
[3] D. A. Engemann, O. Kozynets, D. Sabbagh, G. Lemaître, G. Varoquaux, F. Liem, and A. Gramfort Combining magnetoencephalography with magnetic resonance imaging enhances learning of surrogate-biomarkers. eLife, 9:e54055, 2020 https://elifesciences.org/articles/54055
The filter-bank pipelines (across multiple frequency bands) can the thought of as follows:
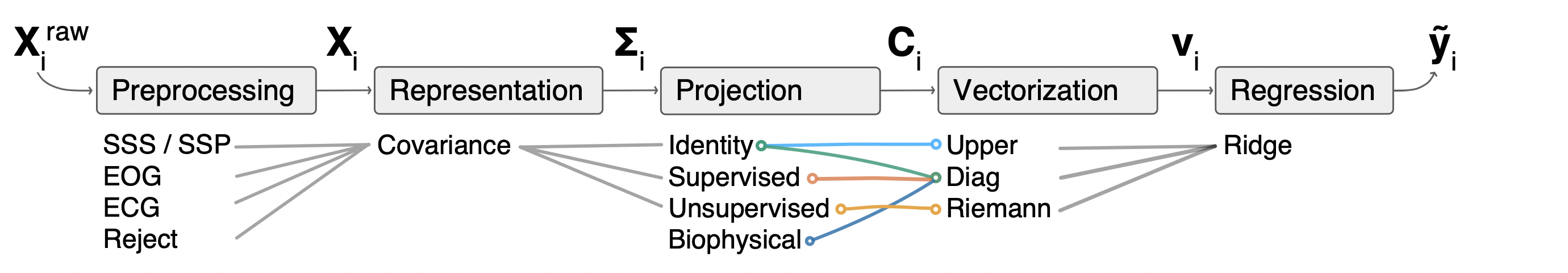
After preprocessing, covariance matrices can be projected to mitigate field spread and deal with rank deficient signals. Subsequently, vectorization is performed to extract column features from the variance, covariance or both. The Riemannian embedding is special in mitigating field spread and providing vectorization in 1 step. It can be combined with dimensionality reduction in the projection step to deal with rank deficiency. Finally, a statistical learning algorithm is applied.
The representation, projection and vectorization steps are separately done for each frequency band.
Installation of Python package
You can clone this library, and then do:
$ pip install -e .
Everything worked if the following command do not return any error:
$ python -c 'import coffeine'
Use with Python
compute_features
Compute power features from raw M/EEG data:
- The power spectral density
- The spectral covariance matrices
- The cospectral covariance matrices
- The cross-frequency covariance matrices
- The cross-frequency correlation matrices
The matrices are of shape (n_frequency_bands, n_channels, n_channels)
Use case example:
import os
import mne
from coffeine import compute_features
data_path = mne.datasets.sample.data_path()
data_dir = os.path.join(data_path, 'MEG', 'sample')
raw_fname = os.path.join(data_dir, 'sample_audvis_raw.fif')
raw = mne.io.read_raw_fif(raw_fname, verbose=False)
# pick some MEG and EEG channels after cropping
raw = raw.copy().crop(0, 200).pick([0, 1, 330, 331, 332])
frequency_bands = {'alpha': (8.0, 15.0), 'beta': (15.0, 30.0)}
features, _ = compute_features(raw, frequency_bands=frequency_bands)
make_filter_bank_models
The following models are implemented:
- riemann
- lw_riemann
- diag
- logdiag
- random
- naive
- spoc
- riemann_wass
- dummy
Use case example:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from coffeine import make_filter_bank_regressor
freq_bands = {'alpha': (8.0, 15.0), 'beta': (15.0, 30.0)}
n_freq_bands = len(freq_bands)
n_subjects = 10
n_channels = 4
# Make toy data
X_cov = np.random.randn(n_subjects, n_freq_bands, n_channels, n_channels)
for sub in range(n_subjects):
for fb in range(n_freq_bands):
X_cov[sub, fb] = X_cov[sub, fb] @ X_cov[sub, fb].T
X_df = pd.DataFrame(
{band: list(X_cov[:, ii]) for ii, band in enumerate(freq_bands)})
X_df['drug'] = np.random.randint(2, size=n_subjects)
y = np.random.randn(len(X_df))
# Models
fb_model = make_filter_bank_regressor(names=freq_bands.keys(),
method='riemann')
fb_model.fit(X_df, y)
Cite
If you use this code please cite:
D. Sabbagh, P. Ablin, G. Varoquaux, A. Gramfort, and D.A. Engemann. Predictive regression modeling with MEG/EEG: from source power to signals and cognitive states. NeuroImage, page 116893,2020. ISSN 1053-8119. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811920303797
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
File details
Details for the file coffeine-0.1.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: coffeine-0.1.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 16.4 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.4.1 importlib_metadata/4.5.0 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.26.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.54.0 CPython/3.8.6
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | d2db48ecbfe255ebdc527ac7dde75efa6ee00d1dcf42dc5e4d35b0bf15948b77 |
|
| MD5 | a79aef73be48225dfa5c82be0592447d |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 0e9b0f9d36e95b23b58a06a2142cf29e60925658a53b4063706f7863da3c0e17 |











