A lightweight top like monitor for linux CGroups
Project description
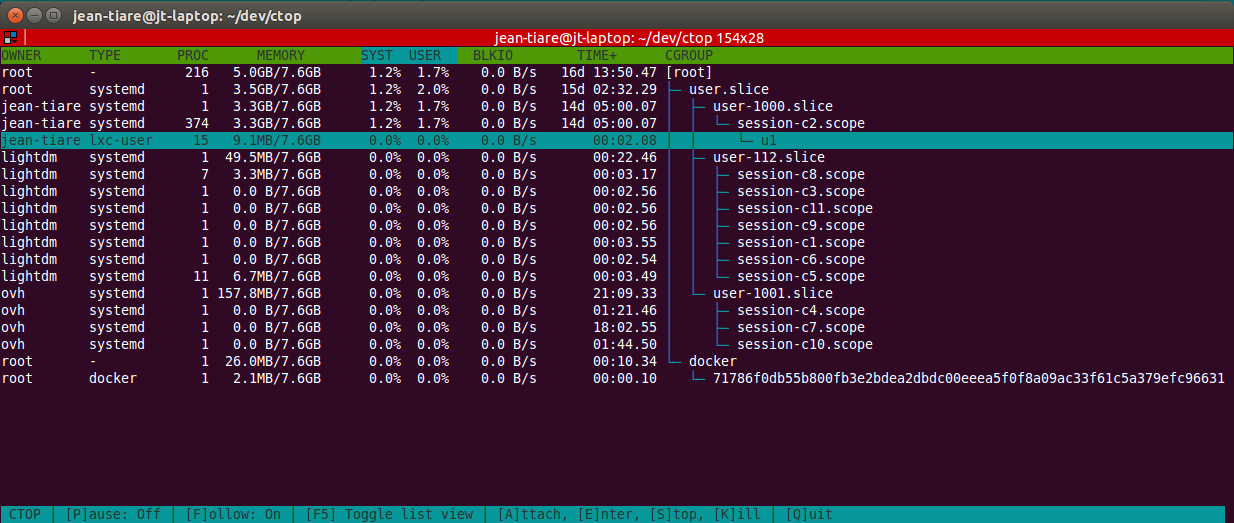
A command line / text based Linux Containers monitoring tool that works just like you expect.
Introduction
ctop will help you see what’s going on at the container level. Basically, containers are a logical group of processes isolated using kernel’s cgroups and namespaces. Recently, they have been made popular by Docker and they are also heavily used under the hood by systemd and a load of container tools like lxc, rocket, lmctfy and many others.
Under the hood, ctop will collect all metrics it can from cgroups in realtime and render them to instantly give you an overview of the global system health.
It currently collects metrics related to cpu, memory and block IO usage as well as metadata such as owning user (mostly for systemd based containers), uptime and attempts to guess the container managing technology behind.
When the container technology has been successfully guessed, additional features are exposed like attaching to container (basically, it opens a shell in the container context) and stopping it.
ctop author uses it on production system to quicky detect biggest memory users in low memory situations.
Features
collect cpu, memory and blkio metrics
collect metadata like task count, owning user, container technology
sort by any column
optionally display logical/tree view
optionally follow selected cgroup/container
optionnaly pause the refresh (typically, to select text)
detects Docker, LXC, unprivileged LXC and systemd based containers
supports advanced features for Docker and LXC based containers
open a shell/attach to supported container types for further diagnose
stop/kill supported container types
click to sort / reverse
click to select cgroup
no external dependencies beyond Python >= 2.6
Installation
As a monitoring tool, ctop tries to be as dicrete as possible. Nonetheless it still has some expectations. It will need at least Python 2.6 with builtin curses support to run. This is usually found with Debian 6 and newer.
This said, the recommended installation method relies on pip
pip install ctop
ctopIf using pip is not an option, which is often the case on production systems, you may also directly grab the self-contained source file directly from github and run it in place. All you’ll need is Python 2.6 (Debian Squeeze):
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/yadutaf/ctop/master/cgroup_top.py -O ctop
chmod +x ctop
./ctopAlternatively, if you are a Boot2docker user, you may install a Dockerized version of ctop instead. Please note that this is experimental and that you may not be able to controll / attach to your containers from ctop using this method:
docker pull yadutaf/ctop
docker run --volume=/sys/fs/cgroup:/sys/fs/cgroup:ro -it --rm yadutaf/ctop
# Optionally, to resolve uids to usernames, add '--volume /etc/passwd:/etc/passwd:ro'Usage
Command line:
Monitor local cgroups as used by Docker, LXC, SystemD, ...
Usage:
ctop [--tree] [--refresh=<seconds>] [--columns=<columns>] [--sort-col=<sort-col>] [--follow=<name>]
ctop (-h | --help)
Options:
--tree Show tree view by default.
--follow=<name> Follow/highlight cgroup at path.
--refresh=<seconds> Refresh display every <seconds> [default: 1].
--columns=<columns> List of optional columns to display. Always includes 'name'. [default: owner,processes,memory,cpu-sys,cpu-user,blkio,cpu-time].
--sort-col=<sort-col> Select column to sort by initially. Can be changed dynamically. [default: cpu-user]
-h --help Show this screen.Control:
press p to toggle/pause the refresh and select text.
press f to let selected line follow / stay on the same container. Default: Don’t follow.
press q or Ctrl+C to quit.
press F5 to toggle tree/list view. Default: list view.
press ↑ and ↓ to navigate between containers.
click on title line to select sort column / reverse sort order.
click on any container line to select it.
Additionally, for supported container types (Currently Docker and LXC):
press a to attach to console output.
press e to open a shell in the container context. Aka ‘enter’ container.
press s to stop the container (SIGTERM).
press k to kill the container (SIGKILL).
Requirements
python >=2.6 with builtin curses support
Licence
MIT
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
File details
Details for the file ctop-0.4.0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: ctop-0.4.0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 10.4 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 0f70d8aa2472cd36ada3a9650211260982bee0f8d55897da5d71b1b136d18a95 |
|
| MD5 | b9ba7ee0cd49514d86d87789a45e306a |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 3cf3c1af97233366ae4b2a23ae437a3bc5a69c2c083b1db4f066c0c7acde19f2 |











