Drag and drop sorting for models and inline models in Django admin.
Project description
Current version: 2.0.20
This project makes it easy to add drag-and-drop ordering to any model in Django admin. Inlines for a sortable model may also be made sortable, enabling individual items or groups of items to be sortable.
Sorting model instances with a sortable parent:
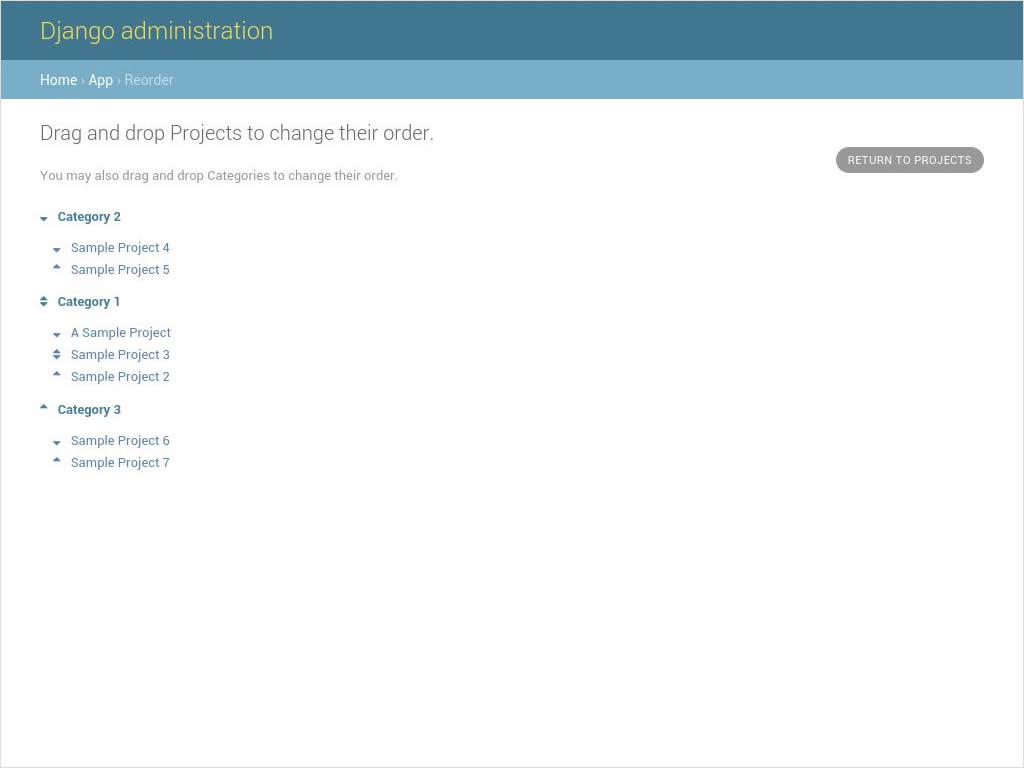
sortable-models
Sorting inlines:
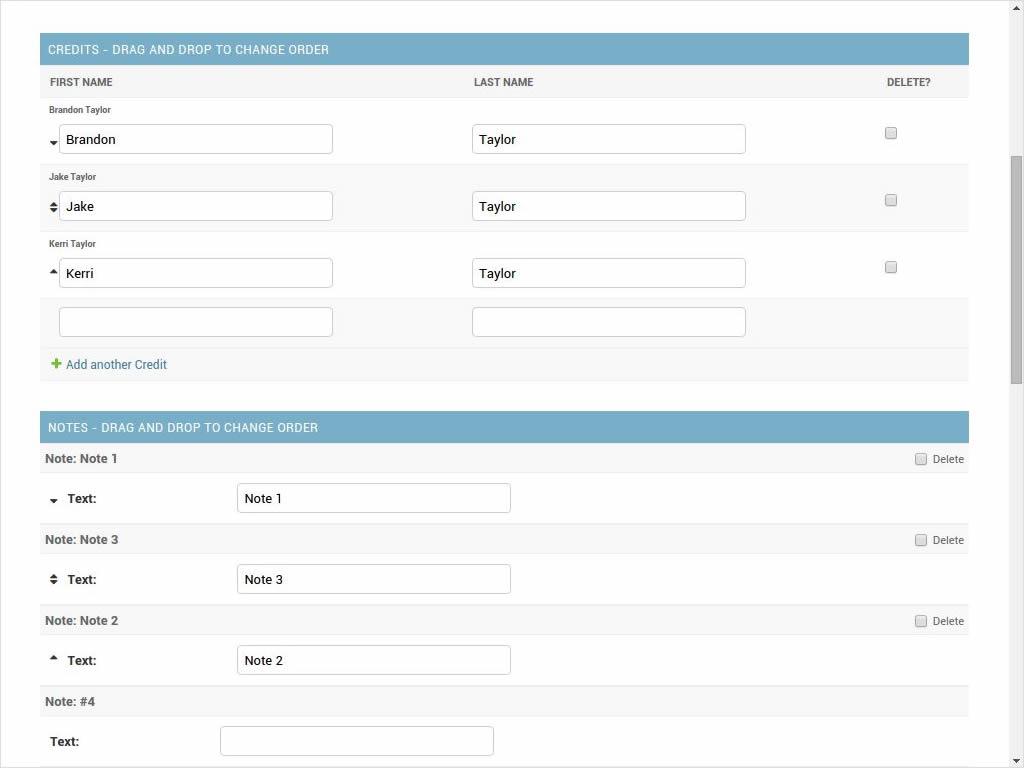
sortable-inlines
Supported Django Versions
For Django 1.5.x to 1.9.x, use version 2.0.18.
For Django 1.10.x, use 2.0.19 or higher.
Other notes of interest regarding versions
django-admin-sortable 1.5.2 introduced backward-incompatible changes for Django 1.4.x
django-admin-sortable 1.6.6 introduced a backward-incompatible change for the sorting_filters attribute. Please convert your attributes to the new tuple-based format if you haven’t already.
django-admin-sortable 1.7.1 and higher are compatible with Python 3.
Installation
$ pip install django-admin-sortable
–or–
Download django-admin-sortable from source
1. Unzip the directory and cd into the uncompressed project directory 2.
Optional: Enable your virtualenv
Run $ python setup.py install or add adminsortable to your PYTHONPATH.
Configuration
Add adminsortable to your INSTALLED_APPS.
Ensure django.core.context_processors.static is in your TEMPLATE_CONTEXT_PROCESSORS.
Ensure that CSRF_COOKIE_HTTPONLY has not been set to True, as django-admin-sortable is currently incompatible with that setting.
Static Media
Preferred: Use the staticfiles app
Alternate: Copy the adminsortable folder from the static folder to the location you serve static files from.
Testing
Have a look at the included sample_project to see working examples. The login credentials for admin are: admin/admin
When a model is sortable, a tool-area link will be added that says “Change Order”. Click this link, and you will be taken to the custom view where you can drag-and-drop the records into order.
Inlines may be drag-and-dropped into any order directly from the change form.
Usage
Models
To add “sortability” to a model, you need to inherit SortableMixin and at minimum, define:
The field which should be used for Meta.ordering, which must resolve to one of the integer fields defined in Django’s ORM:
PositiveIntegerField
IntegerField
PositiveSmallIntegerField
SmallIntegerField
BigIntegerField
Meta.ordering must only contain one value, otherwise, your objects will not be sorted correctly.
It is recommended that you set editable=False and db_index=True on the field defined in Meta.ordering for a seamless Django admin experience and faster lookups on the objects.
Sample Model:
# models.py
from adminsortable.models import SortableMixin
class MySortableClass(SortableMixin):
title = models.CharField(max_length=50)
class Meta:
verbose_name = 'My Sortable Class'
verbose_name_plural = 'My Sortable Classes'
ordering = ['the_order']
# define the field the model should be ordered by
the_order = models.PositiveIntegerField(default=0, editable=False, db_index=True)
def __unicode__(self):
return self.titleSupport for models that don’t use an AutoField for their primary key are also supported in version 2.0.20 or higher.
Common Use Case
A common use case is to have child objects that are sortable relative to a parent. If your parent object is also sortable, here’s how you would set up your models and admin options:
# models.py
from adminsortable.fields import SortableForeignKey
class Category(SortableMixin):
class Meta:
ordering = ['category_order']
verbose_name_plural = 'Categories'
title = models.CharField(max_length=50)
# ordering field
category_order = models.PositiveIntegerField(default=0, editable=False, db_index=True)
class Project(SortableMixin):
class Meta:
ordering = ['project_order']
category = SortableForeignKey(Category)
title = models.CharField(max_length=50)
# ordering field
project_order = models.PositiveIntegerField(default=0, editable=False, db_index=True)
def __unicode__(self):
return self.title
# admin.py
from adminsortable.admin import SortableAdmin
from your_app.models import Category, Project
admin.site.register(Category, SortableAdmin)
admin.site.register(Project, SortableAdmin)Sometimes you might have a parent model that is not sortable, but has child models that are. In that case define your models and admin options as such:
from adminsortable.fields import SortableForeignKey
# models.py
class Category(models.Model):
class Meta:
verbose_name_plural = 'Categories'
title = models.CharField(max_length=50)
...
class Project(SortableMixin):
class Meta:
ordering = ['project_order']
category = SortableForeignKey(Category)
title = models.CharField(max_length=50)
# ordering field
project_order = models.PositiveIntegerField(default=0, editable=False, db_index=True)
def __unicode__(self):
return self.title
# admin
from adminsortable.admin import NonSortableParentAdmin, SortableStackedInline
from your_app.models import Category, Project
class ProjectInline(SortableStackedInline):
model = Project
extra = 1
class CategoryAdmin(NonSortableParentAdmin):
inlines = [ProjectInline]
admin.site.register(Category, CategoryAdmin)The NonSortableParentAdmin class is necessary to wire up the additional URL patterns and JavaScript that Django Admin Sortable needs to make your models sortable. The child model does not have to be an inline model, it can be wired directly to Django admin and the objects will be grouped by the non-sortable foreign key when sorting.
Backwards Compatibility
If you previously used Django Admin Sortable, DON’T PANIC - everything will still work exactly as before *without any changes to your code*. Going forward, it is recommended that you use the new SortableMixin on your models, as pre-2.0 compatibility might not be a permanent thing.
Please note however that the Sortable class still contains the hard-coded order field, and meta inheritance requirements:
# legacy model definition
from adminsortable.models import Sortable
class Project(Sortable):
class Meta(Sortable.Meta):
pass
title = models.CharField(max_length=50)
def __unicode__(self):
return self.titleModel Instance Methods
Each instance of a sortable model has two convenience methods to get the next or previous instance:
.get_next()
.get_previous()By default, these methods will respect their order in relation to a SortableForeignKey field, if present. Meaning, that given the following data:
| Parent Model 1 | | | | Child Model 1 | | | Child Model 2 | | Parent Model 2 | | | | Child Model 3 | | | Child Model 4 | | | Child Model 5 |
“Child Model 2” get_next() would return None “Child Model 3” get_previous would return None
If you wish to override this behavior, pass in: filter_on_sortable_fk=False:
your_instance.get_next(filter_on_sortable_fk=False)You may also pass in additional ORM “extra_filters” as a dictionary, should you need to:
your_instance.get_next(extra_filters={'title__icontains': 'blue'})Adding Sorting to an existing model
Django 1.5.x to 1.6.x
If you’re adding Sorting to an existing model, it is recommended that you use django-south to create a schema migration to add the “order” field to your model. You will also need to create a data migration in order to add the appropriate values for the “order” column.
Example assuming a model named “Category”:
def forwards(self, orm):
for index, category in enumerate(orm.Category.objects.all()):
category.order = index + 1
category.save()See: this link for more information on South Data Migrations.
Django 1.7.x or higher
Since schema migrations are built into Django 1.7, you don’t have to use south, but the process of adding and running migrations is nearly identical. Take a look at the Migrations documentation to get started.
Django Admin Integration
To enable sorting in the admin, you need to inherit from SortableAdmin:
from django.contrib import admin
from myapp.models import MySortableClass
from adminsortable.admin import SortableAdmin
class MySortableAdminClass(SortableAdmin):
"""Any admin options you need go here"""
admin.site.register(MySortableClass, MySortableAdminClass)To enable sorting on TabularInline models, you need to inherit from SortableTabularInline:
from adminsortable.admin import SortableTabularInline
class MySortableTabularInline(SortableTabularInline):
"""Your inline options go here"""To enable sorting on StackedInline models, you need to inherit from SortableStackedInline:
from adminsortable.admin import SortableStackedInline
class MySortableStackedInline(SortableStackedInline):
"""Your inline options go here"""There are also generic equivalents that you can inherit from:
from adminsortable.admin import (SortableGenericTabularInline,
SortableGenericStackedInline)
"""Your generic inline options go here"""If your parent model is not sortable, but has child inlines that are, your parent model needs to inherit from NonSortableParentAdmin:
from adminsortable.admin import (NonSortableParentAdmin,
SortableTabularInline)
class ChildTabularInline(SortableTabularInline):
model = YourModel
class ParentAdmin(NonSortableParentAdmin):
inlines = [ChildTabularInline]Overriding queryset()
django-admin-sortable supports custom queryset overrides on admin models and inline models in Django admin!
If you’re providing an override of a SortableAdmin or Sortable inline model, you don’t need to do anything extra. django-admin-sortable will automatically honor your queryset.
Have a look at the WidgetAdmin class in the sample project for an example of an admin class with a custom queryset() override.
Overriding queryset() for an inline model
This is a special case, which requires a few lines of extra code to properly determine the sortability of your model. Example:
# add this import to your admin.py
from adminsortable.utils import get_is_sortable
class ComponentInline(SortableStackedInline):
model = Component
def queryset(self, request):
qs = super(ComponentInline, self).queryset(request).filter(
title__icontains='foo')
# You'll need to add these lines to determine if your model
# is sortable once we hit the change_form() for the parent model.
if get_is_sortable(qs):
self.model.is_sortable = True
else:
self.model.is_sortable = False
return qsIf you override the queryset of an inline, the number of objects present may change, and adminsortable won’t be able to automatically determine if the inline model is sortable from here, which is why we have to set the is_sortable property of the model in this method.
Sorting subsets of objects
It is also possible to sort a subset of objects in your model by adding a sorting_filters tuple. This works exactly the same as .filter() on a QuerySet, and is applied after get_queryset() on the admin class, allowing you to override the queryset as you would normally in admin but apply additional filters for sorting. The text “Change Order of” will appear before each filter in the Change List template, and the filter groups are displayed from left to right in the order listed. If no sorting_filters are specified, the text “Change Order” will be displayed for the link.
Self-Referential SortableForeignKey
You can specify a self-referential SortableForeignKey field, however the admin interface will currently show a model that is a grandchild at the same level as a child. I’m working to resolve this issue.
Important!
django-admin-sortable 1.6.6 introduced a backwards-incompatible change for sorting_filters. Previously this attribute was defined as a dictionary, so you’ll need to change your values over to the new tuple-based format.
An example of sorting subsets would be a “Board of Directors”. In this use case, you have a list of “People” objects. Some of these people are on the Board of Directors and some not, and you need to sort them independently.
class Person(Sortable):
class Meta(Sortable.Meta):
verbose_name_plural = 'People'
first_name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
last_name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
is_board_member = models.BooleanField('Board Member', default=False)
sorting_filters = (
('Board Members', {'is_board_member': True}),
('Non-Board Members', {'is_board_member': False}),
)
def __unicode__(self):
return '{} {}'.format(self.first_name, self.last_name)Extending custom templates
By default, adminsortable’s change form and change list views inherit from Django admin’s standard templates. Sometimes you need to have a custom change form or change list, but also need adminsortable’s CSS and JavaScript for inline models that are sortable for example.
SortableAdmin has two attributes you can override for this use case:
change_form_template_extends
change_list_template_extendsThese attributes have default values of:
change_form_template_extends = 'admin/change_form.html'
change_list_template_extends = 'admin/change_list.html'If you need to extend the inline change form templates, you’ll need to select the right one, depending on your version of Django. For Django 1.5.x or below, you’ll need to extend one of the following:
templates/adminsortable/edit_inline/stacked-1.5.x.html templates/adminsortable/edit_inline/tabular-inline-1.5.x.html
For Django 1.6.x, extend:
templates/adminsortable/edit_inline/stacked.html templates/adminsortable/edit_inline/tabular.html
A Special Note About Stacked Inlines…
The height of a stacked inline model can dynamically increase, which can make them difficult to sort. If you anticipate the height of a stacked inline is going to be very tall, I would suggest using SortableTabularInline instead.
Django-CMS integration
Django-CMS plugins use their own change form, and thus won’t automatically include the necessary JavaScript for django-admin-sortable to work. Fortunately, this is easy to resolve, as the CMSPlugin class allows a change form template to be specified:
# example plugin
from cms.plugin_base import CMSPluginBase
class CMSCarouselPlugin(CMSPluginBase):
admin_preview = False
change_form_template = 'cms/sortable-stacked-inline-change-form.html'
inlines = [SlideInline]
model = Carousel
name = _('Carousel')
render_template = 'carousels/carousel.html'
def render(self, context, instance, placeholder):
context.update({
'carousel': instance,
'placeholder': placeholder
})
return context
plugin_pool.register_plugin(CMSCarouselPlugin)The contents of sortable-stacked-inline-change-form.html at a minimum need to extend the extrahead block with:
{% extends "admin/cms/page/plugin_change_form.html" %}
{% load static from staticfiles %}
{% block extrahead %}
{{ block.super }}
<script type="text/javascript" src="{% static 'adminsortable/js/jquery-ui-django-admin.min.js' %}"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="{% static 'adminsortable/js/jquery.django-csrf.js' %}"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="{% static 'adminsortable/js/admin.sortable.stacked.inlines.js' %}"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="{% static 'adminsortable/css/admin.sortable.inline.css' %}" />
{% endblock extrahead %}Sorting within Django-CMS is really only feasible for inline models of a plugin as Django-CMS already includes sorting for plugin instances. For tabular inlines, just substitute:
<script src="{% static 'adminsortable/js/admin.sortable.stacked.inlines.js' %}"></script>with:
<script src="{% static 'adminsortable/js/admin.sortable.tabular.inlines.js' %}"></script>Rationale
Other projects have added drag-and-drop ordering to the ChangeList view, however this introduces a couple of problems…
The ChangeList view supports pagination, which makes drag-and-drop ordering across pages impossible.
The ChangeList view by default, does not order records based on a foreign key, nor distinguish between rows that are associated with a foreign key. This makes ordering the records grouped by a foreign key impossible.
The ChangeList supports in-line editing, and adding drag-and-drop ordering on top of that just seemed a little much in my opinion.
Status
django-admin-sortable is currently used in production.
What’s new in 2.0.20?
Support for models that use another type of field besides AutoField for their primary key. Thanks [@rubendura](https://github.com/rubendura).
Future
Better template support for foreign keys that are self referential. If someone would like to take on rendering recursive sortables, that would be super.
License
django-admin-sortable is released under the Apache Public License v2.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
File details
Details for the file django-admin-sortable-2.0.20.zip.
File metadata
- Download URL: django-admin-sortable-2.0.20.zip
- Upload date:
- Size: 113.2 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 5a3015adcf3e66b328d79d23c42b86e572d7acd9e2dc90ded6b9f1a2c3aa43bd |
|
| MD5 | dcc83136e7349246d2a6ef962f79512e |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 660900e49c54bf7758a83c32d7812b115c411e9cf29141e0da7790c6bb916fc2 |













