A Python package for interactive mapping using Google Earth Engine and ipyleaflet
Project description
geemap











Authors: Dr. Qiusheng Wu (https://wetlands.io)
A Python package for interactive mapping with Google Earth Engine, ipyleaflet, and ipywidgets.
GitHub repo: https://github.com/giswqs/geemap
Documentation: https://geemap.readthedocs.io
360+ GEE notebook examples: https://github.com/giswqs/earthengine-py-notebooks
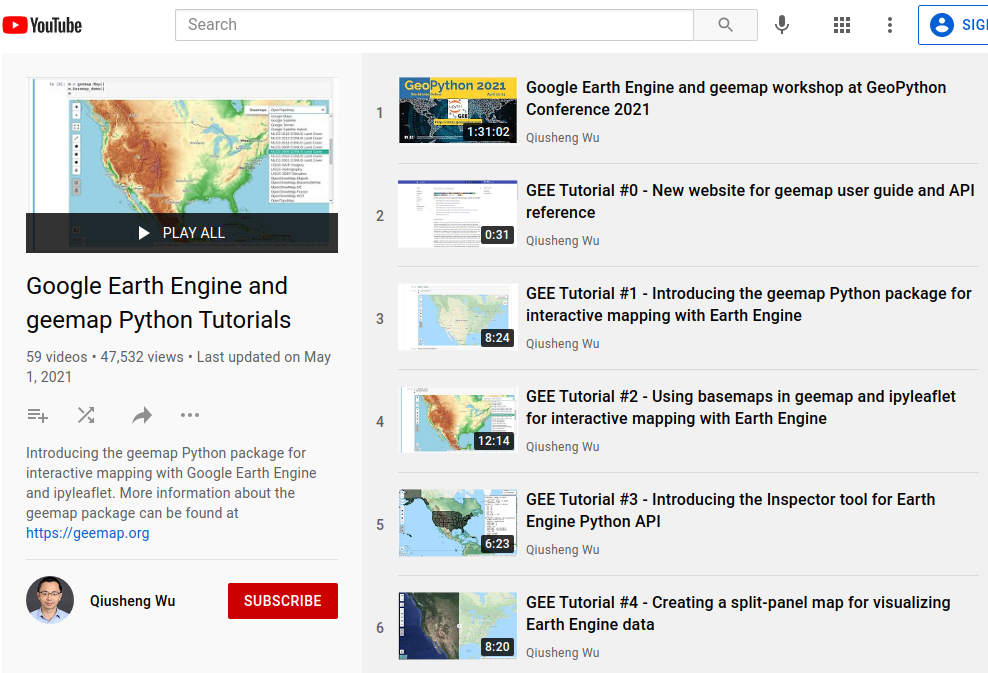
GEE Tutorials on YouTube: https://gishub.org/geemap
Free software: MIT license
Contents
Features
Automated conversion from Earth Engine JavaScripts to Python scripts and Jupyter notebooks.
Displaying Earth Engine data layers for interactive mapping.
Supporting Earth Engine JavaScript API-styled functions in Python, such as Map.addLayer(), Map.setCenter(), Map.centerObject(), Map.setOptions().
Creating split-panel maps with Earth Engine data.
Retrieving Earth Engine data interactively using the Inspector Tool.
Interactive plotting of Earth Engine data by simply clicking on the map.
Converting data format between GeoJSON and Earth Engine.
Using drawing tools to interact with Earth Engine data.
Using shapefiles with Earth Engine without having to upload data to one’s GEE account.
Exporting Earth Engine FeatureCollection to other formats (i.e., shp, csv, json, kml, kmz) using only one line of code.
Exporting Earth Engine Image and ImageCollection as GeoTIFF.
Extracting pixels from an Earth Engine Image into a 3D numpy array.
Installation
The geemap Python package is built upon the ipyleaflet and folium packages and implements several methods for interacting with Earth Engine data layers, such as Map.addLayer(), Map.setCenter(), and Map.centerObject().
To install geemap, run this command in your terminal:
pip install geemapgeemap is also available on conda-forge. If you have Anaconda or Miniconda installed on your computer, you can create a conda Python environment to install geemap:
conda create -n gee python
conda activate gee
conda install -c conda-forge geemapIf you have installed geemap before and want to upgrade to the latest version, you can run the following command in your terminal:
pip install -U geemapIf you use conda, you can update geemap to the latest version by running the following command in your terminal:
conda update -c conda-forge geemapTo install the development version from GitHub, run the following command in your terminal:
pip install git+https://github.com/giswqs/geemapUsage
Important note: A key difference between ipyleaflet and folium is that ipyleaflet is built upon ipywidgets and allows bidirectional communication between the front-end and the backend enabling the use of the map to capture user input, while folium is meant for displaying static data only (source). Note that Google Colab currently does not support ipyleaflet (source). Therefore, if you are using geemap with Google Colab, you should use import geemap.eefolium. If you are using geemap with binder or a local Jupyter notebook server, you can use import geemap, which provides more functionalities for capturing user input (e.g., mouse-clicking and moving).
More GEE Tutorials are available on my YouTube channel.
To create an ipyleaflet-based interactive map:
import geemap
Map = geemap.Map(center=[40,-100], zoom=4)
MapTo create a folium-based interactive map:
import geemap.eefolium as emap
Map = emap.Map(center=[40,-100], zoom=4)
MapTo add an Earth Engine data layer to the Map:
Map.addLayer(ee_object, vis_params, name, shown, opacity)To center the map view at a given coordinates with the given zoom level:
Map.setCenter(lon, lat, zoom)To center the map view around an Earth Engine object:
Map.centerObject(ee_object, zoom)To add LayerControl to a folium-based Map:
Map.addLayerControl()To add a minimap (overview) to an ipyleaflet-based Map:
Map.add_minimap()To add additional basemaps to the Map:
Map.add_basemap('Esri Ocean')
Map.add_basemap('Esri National Geographic')To add an XYZ tile layer to the Map:
url = 'https://mt1.google.com/vt/lyrs=m&x={x}&y={y}&z={z}'
Map.add_tile_layer(url, name='Google Map', attribution='Google')To add a WMS layer to the Map:
naip_url = 'https://services.nationalmap.gov/arcgis/services/USGSNAIPImagery/ImageServer/WMSServer?'
Map.add_wms_layer(url=naip_url, layers='0', name='NAIP Imagery', format='image/png', shown=True)To convert a shapefile to Earth Engine object and add it to the Map:
ee_object = geemap.shp_to_ee(shp_file_path)
Map.addLayer(ee_object, {}, 'Layer name')To convert a GeoJSON file to Earth Engine object and add it to the Map:
ee_object = geemap.geojson_to_ee(geojson_file_path)
Map.addLayer(ee_object, {}, 'Layer name')To download an ee.FeatureCollection as a shapefile:
geemap.ee_to_csv(ee_object, filename, selectors)To export an ee.FeatureCollection to other formats, including shp, csv, json, kml, and kmz:
geemap.ee_export_vector(ee_object, filename, selectors)To export an ee.Image as a GeoTIFF file:
geemap.ee_export_image(ee_object, filename, scale, crs, region, file_per_band)To export an ee.ImageCollection as GeoTIFF files:
geemap.ee_export_image_collection(ee_object, output, scale, crs, region, file_per_band)To extract pixels from an ee.Image into a 3D numpy array:
geemap.ee_to_numpy(ee_object, bands, region, properties, default_value)To create a split-panel Map:
Map.split_map(left_layer='HYBRID', right_layer='ESRI')To add a marker cluster to the Map:
Map.marker_cluster()
feature_collection = ee.FeatureCollection(Map.ee_markers)To convert all GEE JavaScripts in a folder recursively to Python scripts:
from geemap.conversion import *
js_to_python_dir(in_dir, out_dir)To convert all GEE Python scripts in a folder recursively to Jupyter notebooks:
from geemap.conversion import *
template_file = get_nb_template()
py_to_ipynb_dir(in_dir, template_file, out_dir)To execute all Jupyter notebooks in a folder recursively and save output cells:
from geemap.conversion import *
execute_notebook_dir(in_dir)Examples
The following examples require the geemap package, which can be installed using pip install geemap. Check the Installation section for more information. More examples can be found at another repo: A collection of 300+ Jupyter Python notebook examples for using Google Earth Engine with interactive mapping.
Converting GEE JavaScripts to Python scripts and Jupyter notebooks
Launch an interactive notebook with Google Colab. Keep in mind that the conversion might not always work perfectly. Additional manual changes might still be needed. ui and chart are not supported. The source code for this automated conversion module can be found at conversion.py.

import os
from geemap.conversion import *
# Create a temporary working directory
work_dir = os.path.join(os.path.expanduser('~'), 'geemap')
# Get Earth Engine JavaScript examples. There are five examples in the geemap package folder.
# Change js_dir to your own folder containing your Earth Engine JavaScripts, such as js_dir = '/path/to/your/js/folder'
js_dir = get_js_examples(out_dir=work_dir)
# Convert all Earth Engine JavaScripts in a folder recursively to Python scripts.
js_to_python_dir(in_dir=js_dir, out_dir=js_dir, use_qgis=True)
print("Python scripts saved at: {}".format(js_dir))
# Convert all Earth Engine Python scripts in a folder recursively to Jupyter notebooks.
nb_template = get_nb_template() # Get the notebook template from the package folder.
py_to_ipynb_dir(js_dir, nb_template)
# Execute all Jupyter notebooks in a folder recursively and save the output cells.
execute_notebook_dir(in_dir=js_dir)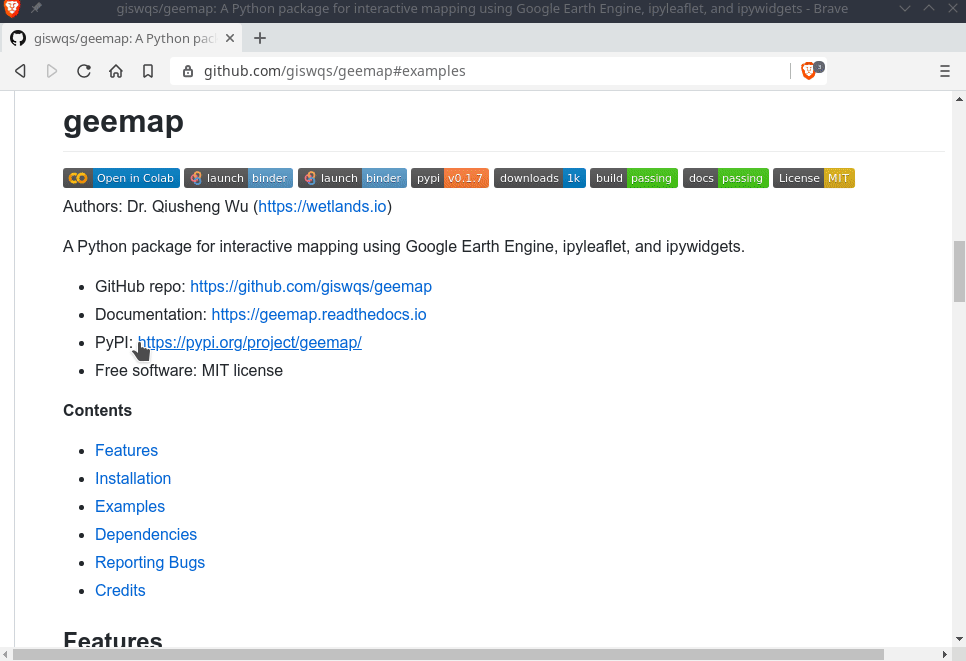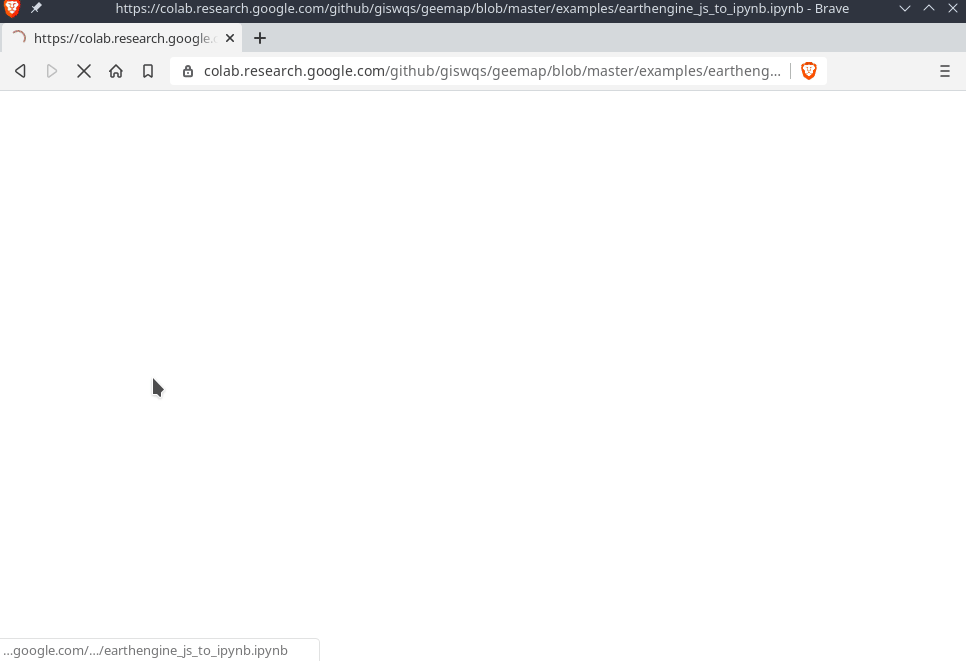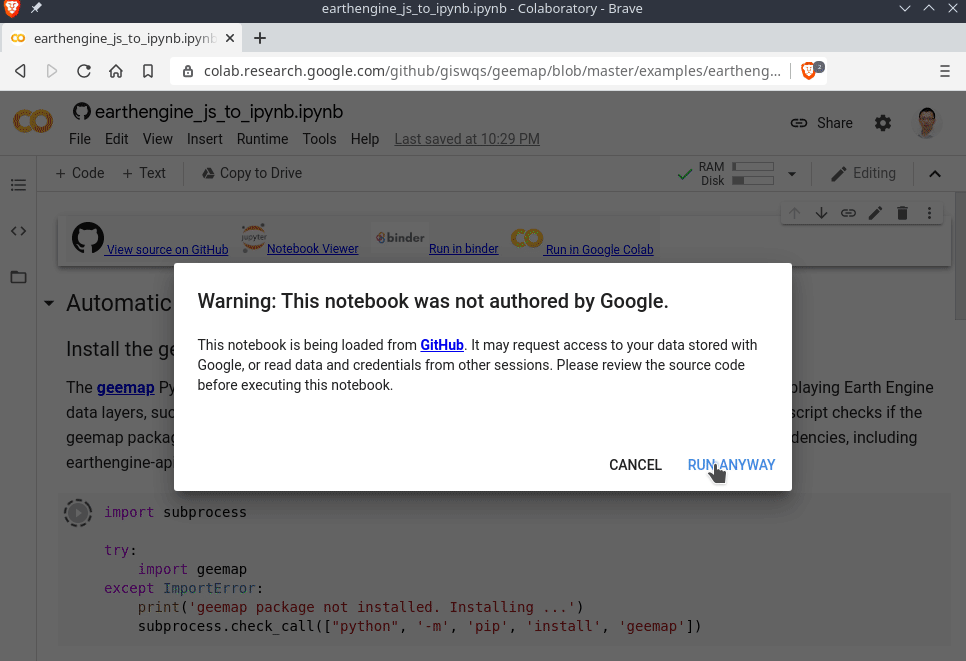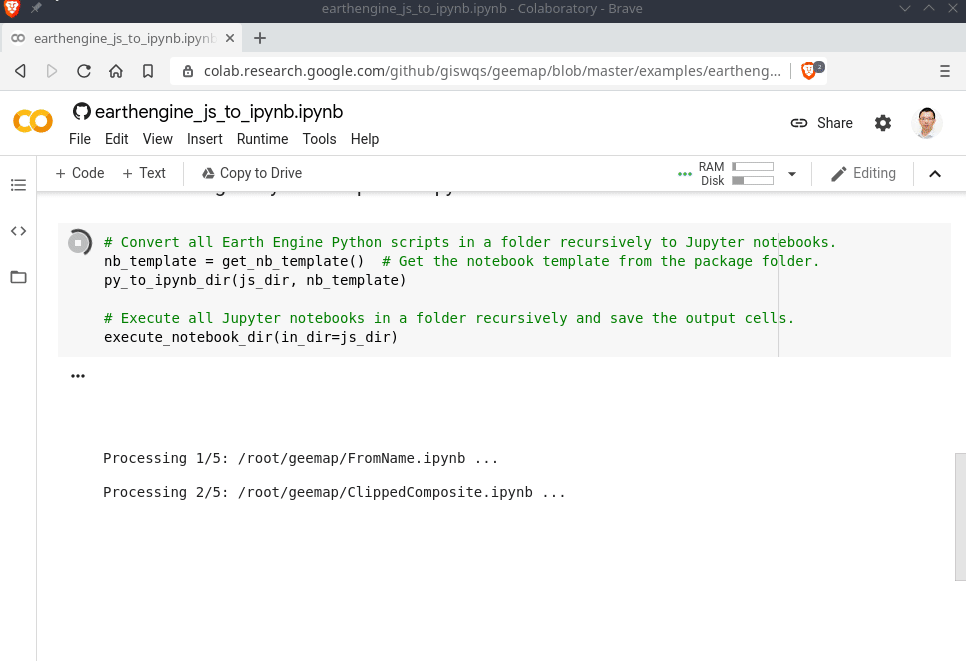
Interactive mapping using GEE Python API and geemap
Launch an interactive notebook with Google Colab. Note that Google Colab currently does not support ipyleaflet. Therefore, you should use import geemap.eefolium instead of import geemap.

# Installs geemap package
import subprocess
try:
import geemap
except ImportError:
print('geemap package not installed. Installing ...')
subprocess.check_call(["python", '-m', 'pip', 'install', 'geemap'])
# Checks whether this notebook is running on Google Colab
try:
import google.colab
import geemap.eefolium as emap
except:
import geemap as emap
# Authenticates and initializes Earth Engine
import ee
try:
ee.Initialize()
except Exception as e:
ee.Authenticate()
ee.Initialize()
# Creates an interactive map
Map = emap.Map(center=[40,-100], zoom=4)
# Adds Earth Engine dataset
image = ee.Image('USGS/SRTMGL1_003')
# Sets visualization parameters.
vis_params = {
'min': 0,
'max': 4000,
'palette': ['006633', 'E5FFCC', '662A00', 'D8D8D8', 'F5F5F5']}
# Prints the elevation of Mount Everest.
xy = ee.Geometry.Point([86.9250, 27.9881])
elev = image.sample(xy, 30).first().get('elevation').getInfo()
print('Mount Everest elevation (m):', elev)
# Adds Earth Engine layers to Map
Map.addLayer(image, vis_params, 'SRTM DEM', True, 0.5)
Map.addLayer(xy, {'color': 'red'}, 'Mount Everest')
Map.setCenter(100, 40, 4)
# Map.centerObject(xy, 13)
# Display the Map
Map.addLayerControl()
Map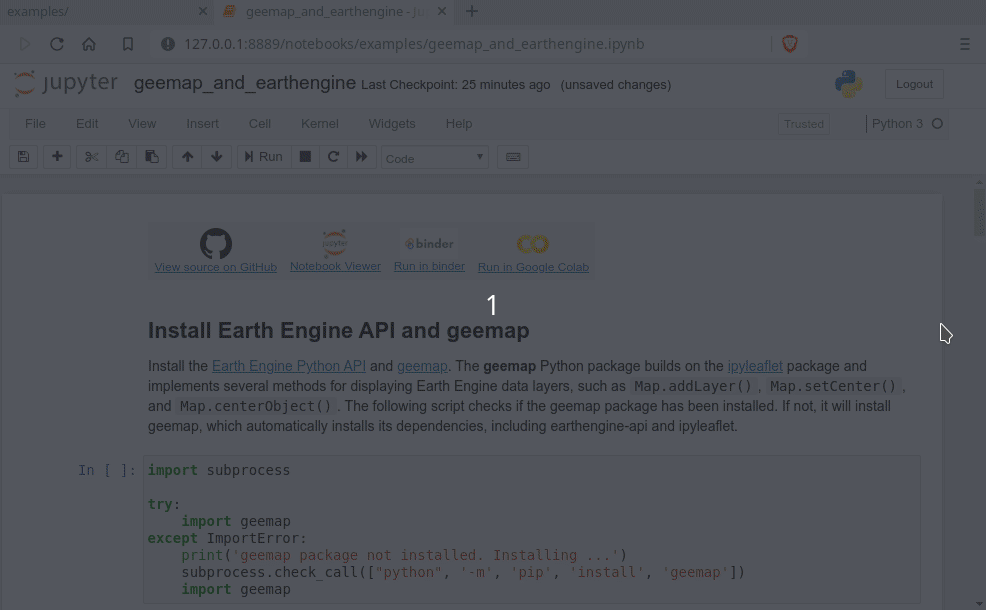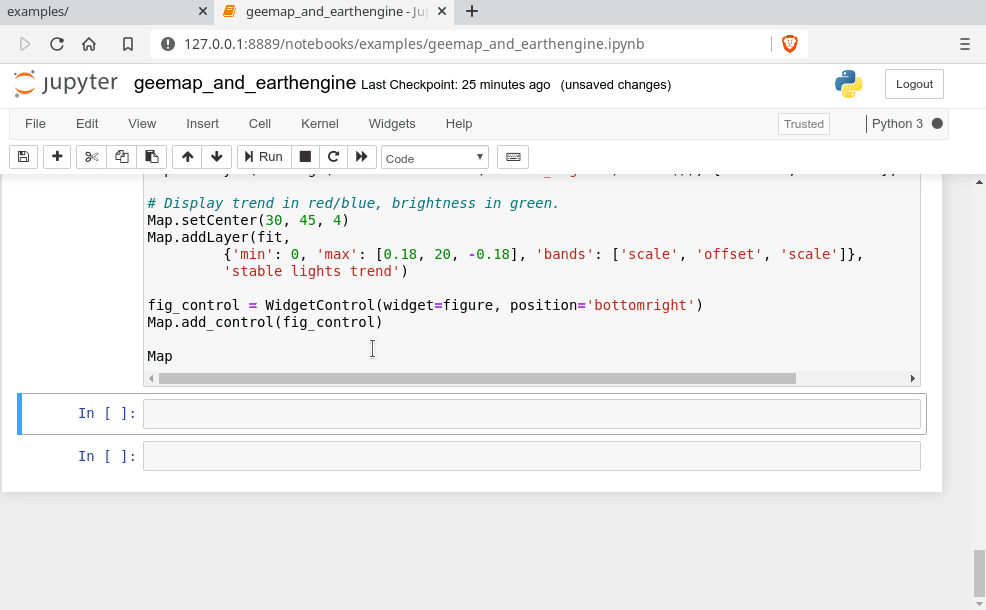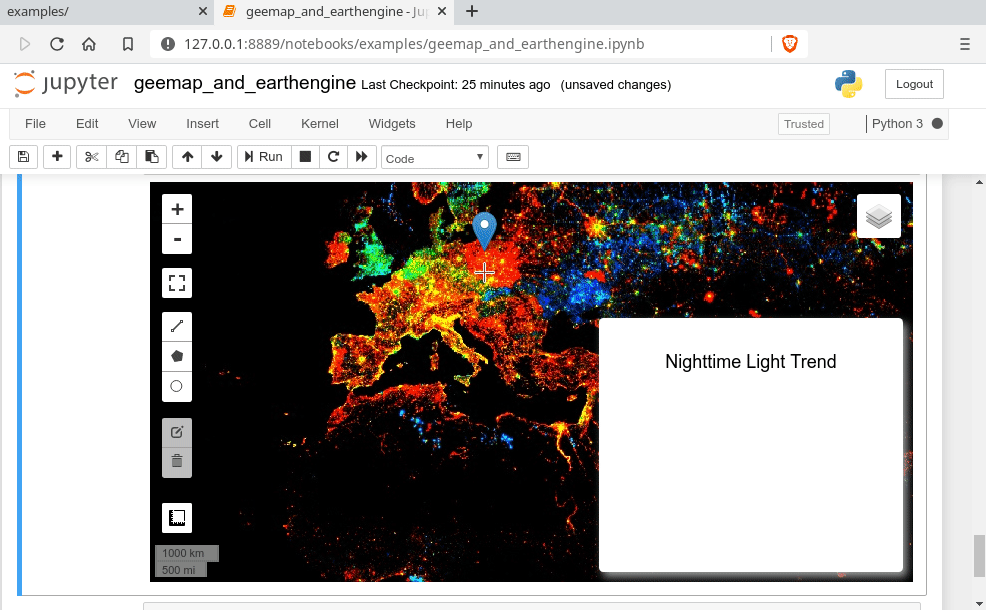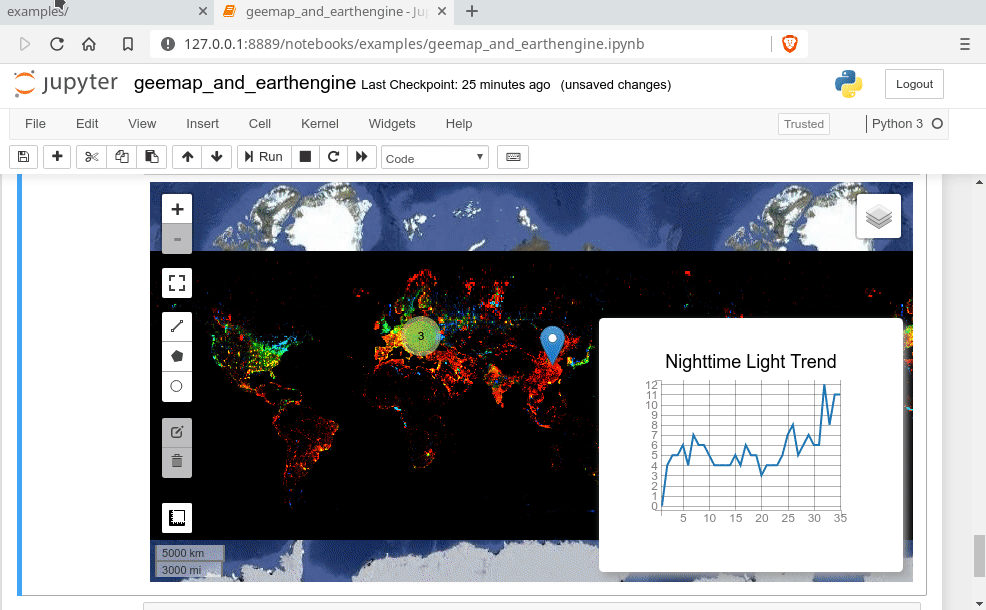
Dependencies
Reporting Bugs
Report bugs at https://github.com/giswqs/geemap/issues.
If you are reporting a bug, please include:
Your operating system name and version.
Any details about your local setup that might be helpful in troubleshooting.
Detailed steps to reproduce the bug.
Credits
This package was created with Cookiecutter and the audreyr/cookiecutter-pypackage project template.
History
0.4.0 (2020-03-19)
0.3.0 (2020-03-18)
0.2.0 (2020-03-17)
0.1.0 (2020-03-08)
First release on PyPI.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
File details
Details for the file geemap-0.6.3.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: geemap-0.6.3.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 49.8 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.1.1 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.23.0 setuptools/46.1.3 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.45.0 CPython/3.8.0
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | e273d5774f19f3adb3db3aa249ee456395e6fb447223bd2b26d6ebde652b44d5 |
|
| MD5 | 0bf11d13e6e4c84bb37cf406ef053ada |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | a4fa587a9771817761732db36cdca53e40d266de1afb6320ff023e38f1ad3435 |
File details
Details for the file geemap-0.6.3-py2.py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: geemap-0.6.3-py2.py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 42.6 kB
- Tags: Python 2, Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.1.1 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.23.0 setuptools/46.1.3 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.45.0 CPython/3.8.0
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | cbff3df74e193ff1d4b265e28cdaf7a71714b7f28d605884c78d00ee1d683fa9 |
|
| MD5 | 59dde0d893488d73706e67fc10b68bcb |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | cff4c3a9fb374a80372a358c39d16e4bb8a190c604598a404857eb45f68b30eb |