GridRoyale - A life simulation for exploring social dynamics
Project description
GridRoyale
View the live version here!
GridRoyale is a life simulation. It's a tool for machine learning researchers to explore social dynamics.
It's similar to Game of Life or GridWorld, except I added game mechanics to encourage the players to behave socially. These game mechanics are similar to those in the battle royale genre of computer games, which is why it's called GridRoyale.
The game mechanics, Python framework and visualization are pretty good-- The core algorithm sucks, and I'm waiting for someone better than me to come and write a new one. If that's you, please open a pull request.
Let's back up for a bit
This project is difficult to explain, and it's also one I've been dreaming of doing for years. Please bear with me as I do my best to explain it in the paragraphs below. I'll also note that I'm a newbie at machine learning and specifically reinforcement learning, so it's quite likely that there is lots of relevant research I'm not familiar with.
My goal is to explore social dynamics.
Like most everyone, I spend a lot of time thinking why people do what they do. How they behave with each other, how they communicate, and how they decide whether they're friends, enemies, or anything murky in between. Sometimes people behave in ways that can be easily analyzed logically, and sometimes they don't. Even when they behave in ways that seem unreasonable, I know it's mostly because my reasoning isn't advanced enough.
That's obviously a very deep rabbit hole to go into. My guiding principle is this: Social behaviors that we see in the world go through a process that's kind of like evolution, meaning survival of the fittest. There are lots of people in the world, they live for a long time and they get to try lots of different behaviors. Behaviors that don't make some kind of sense, don't survive. If you see someone behaving in some way, and that person made it safely to adulthood without drinking bleach from the under-sink cabinet in the kitchen, then in some way that behavior is "the fittest" or close to it, whatever "fittest" means.
Whatever theory we have about why people do what they do, it all starts with trying to survive, and then building layers of abstraction on top of that.
Let's cut back to the technical side of the project: Reinforcement learning, game theory, neural networks, and Canvas animations in the browser.
My thinking is, maybe I can create a simulation where creatures move about in a virtual world. Maybe I can set up the rules of that world to be as conducive as possible to social behaviors. Then I'd see these creatures engage in social behaviors in ways that are totally unscripted, and motivated only by their desire to survive. I could analyze what they do, why, what works and what doesn't. For any behavior that seems unreasonable, I could perform an unlimited number of experiments to find where it is useful, and what would happen if it were removed. I could go backward and forward in time, create parallel realities, and basically have full freedom to run any kind of scenario.
I'm hoping I could use that to model human behaviors in the real world.
I could use neural networks to optimize the creatures' behaviors according to the rewards that they get, use Python to manage the state of the world and make it easy for people to write different policies for the creatures to use, and then display the simulation in a nice Canvas animation in the browser.
I started working on this project in June of 2020. This included giving myself a crash course in neural networks (brag), reinforcement learning and JavaScript animation. As I'm writing these lines (October 2020) I have to stop working on this project, because I'm starting a new full-time job. I'll describe what I did and what I'd like to see, and I hope that other people will be interested in continuing this research.
What I did so far
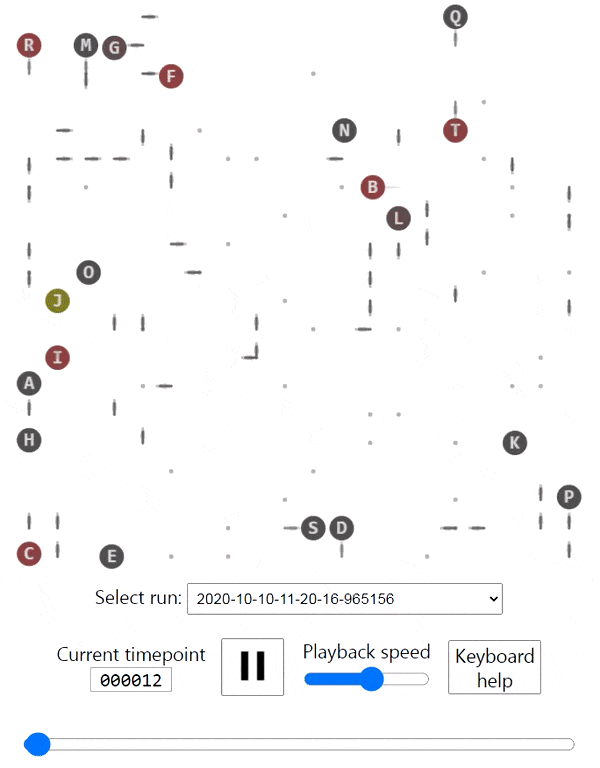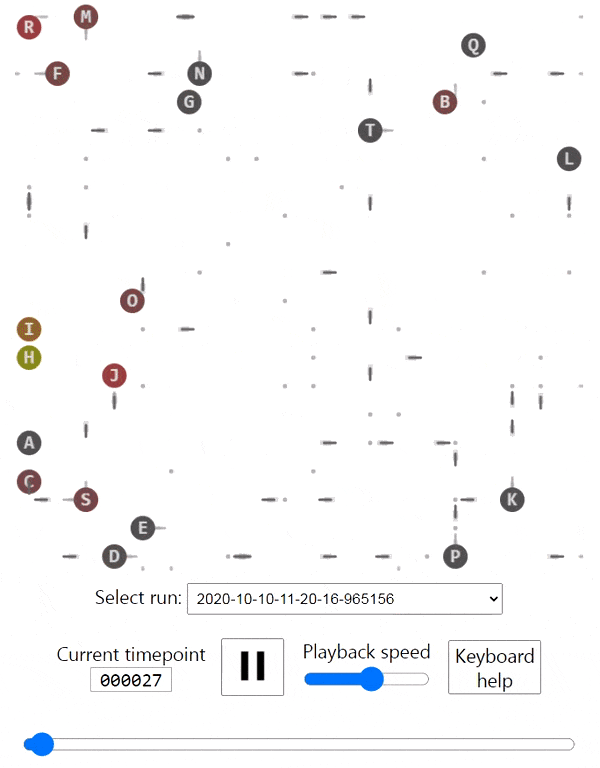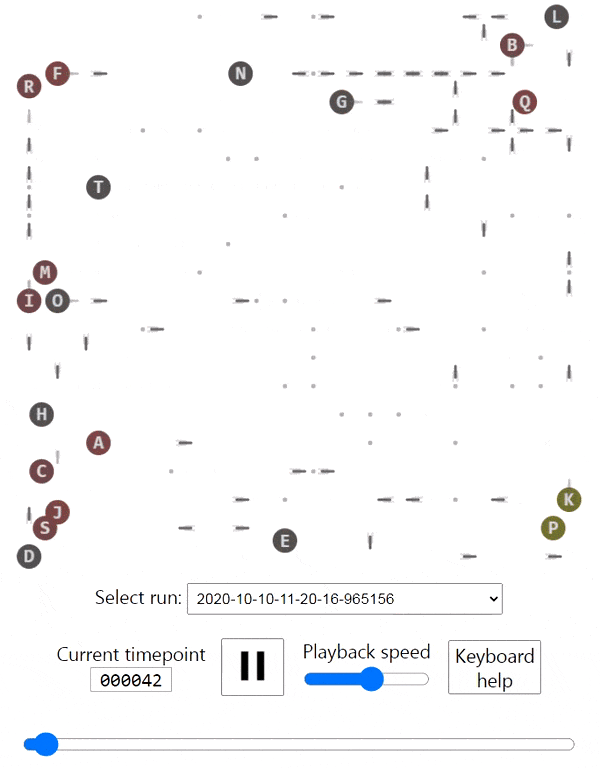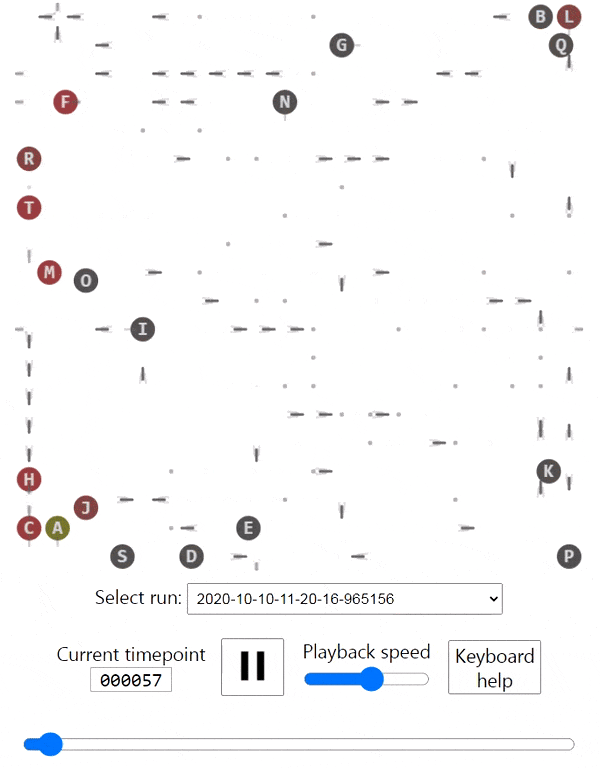
The creatures are able to walk around, eat food that's spawned in random cells in the grid, bump into each other and shoot each other. Eating a piece of food grants the creature 10 points. Bumping into another creature costs 5 points. Getting shot costs 10 points.
I used Keras to write a Q-learning algorithm with a neural network, and that got them to learn how to walk towards the food and avoid bumping into each other. They're not smart enough yet to avoid bullets or have a policy.
There's a nice browser interface that lets you see the entire animation and skip to any timepoint you'd like.
What behaviors I'd like to see
Here's a study that was done at Facebook AI Research. If you're too lazy to read the whole thing, they trained bots to negotiate with each other for items they're trading, and the bots gradually learned how to be shrewd and get better deals. They used a language to communicate between themselves and they learned to give the words their own meaning.
That research has good examples for things I want to see, and good examples for things that are the opposite of what I'd like to see.
Yes, I'd like to see creatures communicating with each other and working to become richer. What I don't want is to have these interactions be so scripted. I don't want the creatures to have predefined tasks, and predefined sessions in which they communicate using predefined words. I want all of their social behavior to be spontaneous and built on top of their basic survival routine. I want them to live in an open world, in which they decide whether they'd like to communicate or not. I don't want episodes of communication that have a clear start and end, I want communication to be a part of the creatures' movement.
This is getting pretty abstract, so let me give an example.
I've already got creatures that know how to go for food and avoid bumping into other creatures. That's a start. Now, imagine that creature X becomes smart enough to figure out that if they get close to other creatures, these other creatures are going to walk away, because they'd like to avoid confrontation. Creature X can therefore establish a territory, i.e. a block of space that no other creatures would step into. This means that creature X could eat all the food that's randomly spawned in its territory. It also needs to routinely patrol the edges of its territory so it could chase away any intruders. This can get difficult if there are several intruders at a time.
A territory is an interesting thing. It's more of a game theory concept than a physical concept. Territories exist outside of physical space, like in intellectual property or internet domain names. The basic condition that makes territories possible is that a player has enough incentive to be stubborn and not give up on the property no matter what, and then can convince the other players of how stubborn it is. It's a combination of cooperation and conflict, since both sides are fighting over territory, but they also have an interest to end the war as quickly as possible. That's what makes it so interesting to study.
Say that the other creatures have also learned this territorial behavior. Each creature now has its own territory, and that territory is bordered by its neighbors' territories. Some borders will be more peaceful, and others will have fights over territory on them, resulting in one side getting a bit of the other's territory.
If you're creature X and you have a few neighbors, you can recognize that some of them get into more fights with you than others. The neighbors that tend not to pick fights at the borders are now your assets. You save so much time by not having to patrol that part of your territory. This means that if one of these good neighbors get attacked, it will be in your interest to help them win. If they'll be pushed aside by a more aggressive creature, that creature might invade your territory later.
Now we have communication and cooperation that are emergent phenomena. We can have complex relationship between creatures, and hopefully something resembling a society.
Another thing that's important to me is that I want things to be visual. I don't want people to have to read a research paper to understand how the creatures are cooperating, I want them to see the creatures doing that. That's why I chose to use Canvas animations in the browser, so people could play with the results without having to install anything.
How to run this code
Installation:
$ pip install grid_royale
Run the server:
$ grid_royale play
This will automatically open a browser window and show you your simulation.
How to extend this code
The creatures' policy is defined by the Policy
class class. Most of
its logic is defined by the more general ModelFreeLearningPolicy
class,
which defines a neural network and uses it to decide on actions. You can change the logic in any of
these classes and see what changes come out in the simulation. The main two methods that get called
by outside code are decide_action_for_observation and train.
I wrote the code to be nice and modular, so when you're writing your logic in the Policy class,
you don't need to think at all about maintaining the rules of the game or showing the animation. The
decide_action_for_observation method gets an observation of the world and needs to return an
action, and all the rest is taken care of.
Either clone the repo or run pip install -e grid_royale, then change the code. Run it using
grid_royale play and see how your creatures fare.
If you'd like to discuss your approach or need help, either open an issue or email me at ram@rachum.com
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
File details
Details for the file grid_royale-0.3.0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: grid_royale-0.3.0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 216.8 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.1.1 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.24.0 setuptools/53.0.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.45.0 CPython/3.8.1
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 021f409e825b5547501a24c85d92feb6e9785948b3651dc0b8b718e43e04d1d2 |
|
| MD5 | 3d2fe98dafa959e134a4d823a412db93 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 7496f7ca11841cdb4aadb4330ce96780edf1112896ae0d17062b8d7dee72285b |
File details
Details for the file grid_royale-0.3.0-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: grid_royale-0.3.0-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 220.5 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.1.1 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.24.0 setuptools/53.0.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.45.0 CPython/3.8.1
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | ccdd5bc3ef24e307b7381deb130d687b962ec8fda46e86fbed50fde3b6fd92cc |
|
| MD5 | 70466eeb1bf31f7836ae704a12e3458d |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 1463ca50d91a416f41c9bae41aed3005ebf539fb056a5dcfd5f108ca141bc781 |