Workflow mgmgt + task scheduling + dependency resolution.
Project description





Luigi is a Python (3.6, 3.7, 3.8, 3.9, 3.10 tested) package that helps you build complex pipelines of batch jobs. It handles dependency resolution, workflow management, visualization, handling failures, command line integration, and much more.
Getting Started
Run pip install luigi to install the latest stable version from PyPI. Documentation for the latest release is hosted on readthedocs.
Run pip install luigi[toml] to install Luigi with TOML-based configs support.
For the bleeding edge code, pip install git+https://github.com/spotify/luigi.git. Bleeding edge documentation is also available.
Background
The purpose of Luigi is to address all the plumbing typically associated with long-running batch processes. You want to chain many tasks, automate them, and failures will happen. These tasks can be anything, but are typically long running things like Hadoop jobs, dumping data to/from databases, running machine learning algorithms, or anything else.
There are other software packages that focus on lower level aspects of data processing, like Hive, Pig, or Cascading. Luigi is not a framework to replace these. Instead it helps you stitch many tasks together, where each task can be a Hive query, a Hadoop job in Java, a Spark job in Scala or Python, a Python snippet, dumping a table from a database, or anything else. It’s easy to build up long-running pipelines that comprise thousands of tasks and take days or weeks to complete. Luigi takes care of a lot of the workflow management so that you can focus on the tasks themselves and their dependencies.
You can build pretty much any task you want, but Luigi also comes with a toolbox of several common task templates that you use. It includes support for running Python mapreduce jobs in Hadoop, as well as Hive, and Pig, jobs. It also comes with file system abstractions for HDFS, and local files that ensures all file system operations are atomic. This is important because it means your data pipeline will not crash in a state containing partial data.
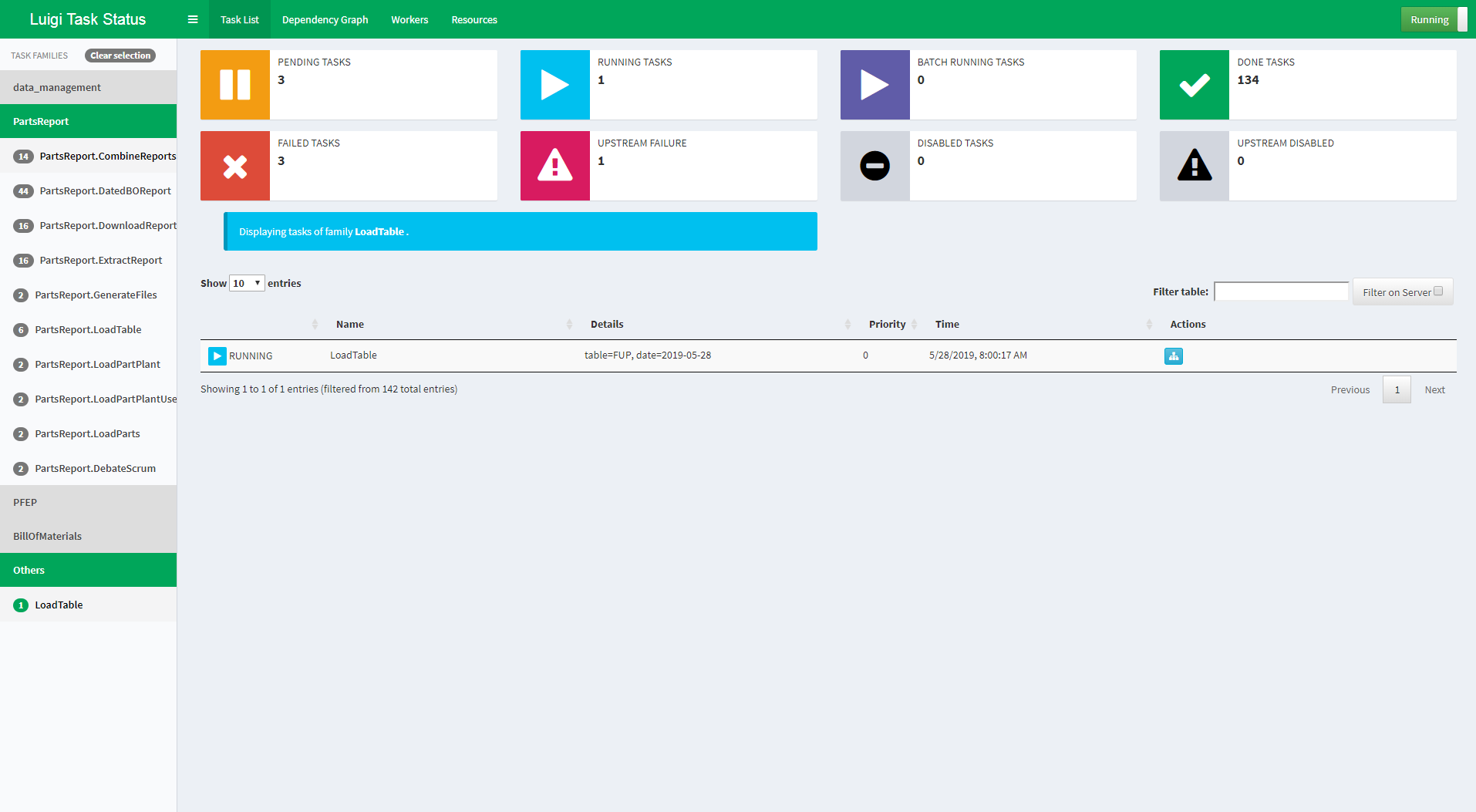
Visualiser page
The Luigi server comes with a web interface too, so you can search and filter among all your tasks.
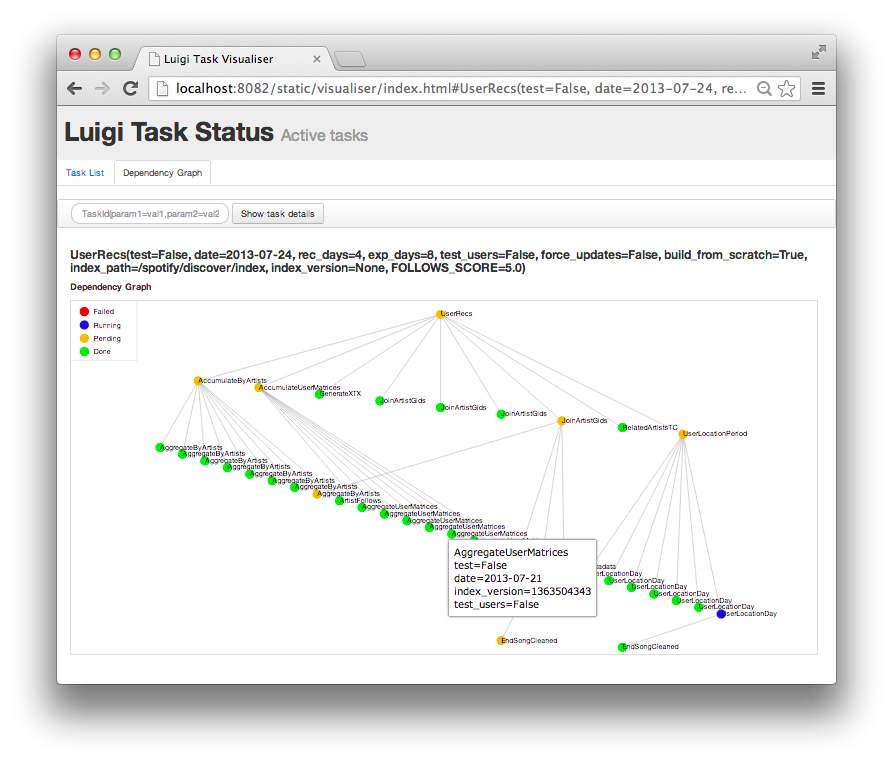
Dependency graph example
Just to give you an idea of what Luigi does, this is a screen shot from something we are running in production. Using Luigi’s visualiser, we get a nice visual overview of the dependency graph of the workflow. Each node represents a task which has to be run. Green tasks are already completed whereas yellow tasks are yet to be run. Most of these tasks are Hadoop jobs, but there are also some things that run locally and build up data files.
Philosophy
Conceptually, Luigi is similar to GNU Make where you have certain tasks and these tasks in turn may have dependencies on other tasks. There are also some similarities to Oozie and Azkaban. One major difference is that Luigi is not just built specifically for Hadoop, and it’s easy to extend it with other kinds of tasks.
Everything in Luigi is in Python. Instead of XML configuration or similar external data files, the dependency graph is specified within Python. This makes it easy to build up complex dependency graphs of tasks, where the dependencies can involve date algebra or recursive references to other versions of the same task. However, the workflow can trigger things not in Python, such as running Pig scripts or scp’ing files.
Who uses Luigi?
We use Luigi internally at Spotify to run thousands of tasks every day, organized in complex dependency graphs. Most of these tasks are Hadoop jobs. Luigi provides an infrastructure that powers all kinds of stuff including recommendations, toplists, A/B test analysis, external reports, internal dashboards, etc.
Since Luigi is open source and without any registration walls, the exact number of Luigi users is unknown. But based on the number of unique contributors, we expect hundreds of enterprises to use it. Some users have written blog posts or held presentations about Luigi:
17zuoye (presentation, 2015)
Uppsala University (tutorial) / (presentation, 2015) / (slides, 2015) / (poster, 2015) / (paper, 2016) / (project)
Some more companies are using Luigi but haven’t had a chance yet to write about it:
We’re more than happy to have your company added here. Just send a PR on GitHub.
External links
Mailing List for discussions and asking questions. (Google Groups)
Releases (PyPI)
Source code (GitHub)
Hubot Integration plugin for Slack, Hipchat, etc (GitHub)
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
File details
Details for the file luigi-3.2.1.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: luigi-3.2.1.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 1.2 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.2 CPython/3.8.16
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 54a2932d0682c15d93695473ba115157a40f503f54e5c5714997e4b68a5e625c |
|
| MD5 | 2af9d2656f0df13c8f4f0dad5f998794 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | f88cd8354945b6d181bc03ccb2c6b87d8e691b9c2fb6f08422b0c3ebf1fc63de |
























