A security focused static analysis platform targeting Android.
Project description
Mariana Trench
Mariana Trench is a security focused static analysis platform targeting Android.
This guide will walk you through setting up Mariana Trench on your machine and get you to find your first remote code execution vulnerability in a small sample app. These instructions are also available at our website.
Prerequisites
Mariana Trench requires a recent version of Python. On MacOS you can get a current version through homebrew:
$ brew install python3
On a Debian flavored Linux (Ubuntu, Mint, Debian), you can use apt-get:
$ sudo apt-get install python3 python3-pip python3-venv
This guide also assumes you have the Android SDK installed and an environment variable $ANDROID_SDK pointed to the location of the SDK.
For the rest of this guide, we assume that you are working inside of a virtual environment. You can set this up with
$ python3 -m venv ~/.venvs/mariana-trench
$ source ~/.venvs/mariana-trench/bin/activate
(mariana-trench)$
The name of the virtual environment in front of your shell prompt indicates that the virtual environment is active.
Installing Mariana Trench
Inside your virtual environment installing Mariana Trench is as easy as running
(mariana-trench)$ pip install mariana-trench
Note: pip install is not currently supported for Apple silicon Macs, you can build from source using the instructions in the Developer's Guide.
Running Mariana Trench
We'll use a small app that is part of our documentation. You can get it by running
(mariana-trench)$ git clone https://github.com/facebook/mariana-trench
(mariana-trench)$ cd mariana-trench/
We are now ready to run the analysis
(mariana-trench)$ mariana-trench \
--system-jar-configuration-path=$ANDROID_SDK/platforms/android-32/android.jar \
--model-generator-configuration-paths=configuration/default_generator_config.json \
--lifecycles-paths=configuration/lifecycles.json \
--rules-paths=configuration/rules.json \
--apk-path=documentation/sample-app/app/build/outputs/apk/debug/app-debug.apk \
--source-root-directory=documentation/sample-app/app/src/main/java \
--model-generator-search-paths=configuration/model-generators/
# ...
INFO Analyzed 68937 models in 7.47s. Found 9 issues!
# ...
The analysis has found 9 issues in our sample app. The output of the analysis is a set of specifications for each method of the application.
Post Processing
The specifications themselves are not meant to be read by humans. We need an additional processing step in order to make the results more presentable. We do this with SAPP PyPi installed for us:
(mariana-trench)$ sapp --tool=mariana-trench analyze .
(mariana-trench)$ sapp --database-name=sapp.db server --source-directory=documentation/sample-app/app/src/main/java
# ...
2021-05-12 12:27:22,867 [INFO] * Running on http://localhost:13337/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
The last line of the output tells us that SAPP started a local webserver that lets us look at the results. Open the link and you will see the 4 issues found by the analysis.
Exploring Results
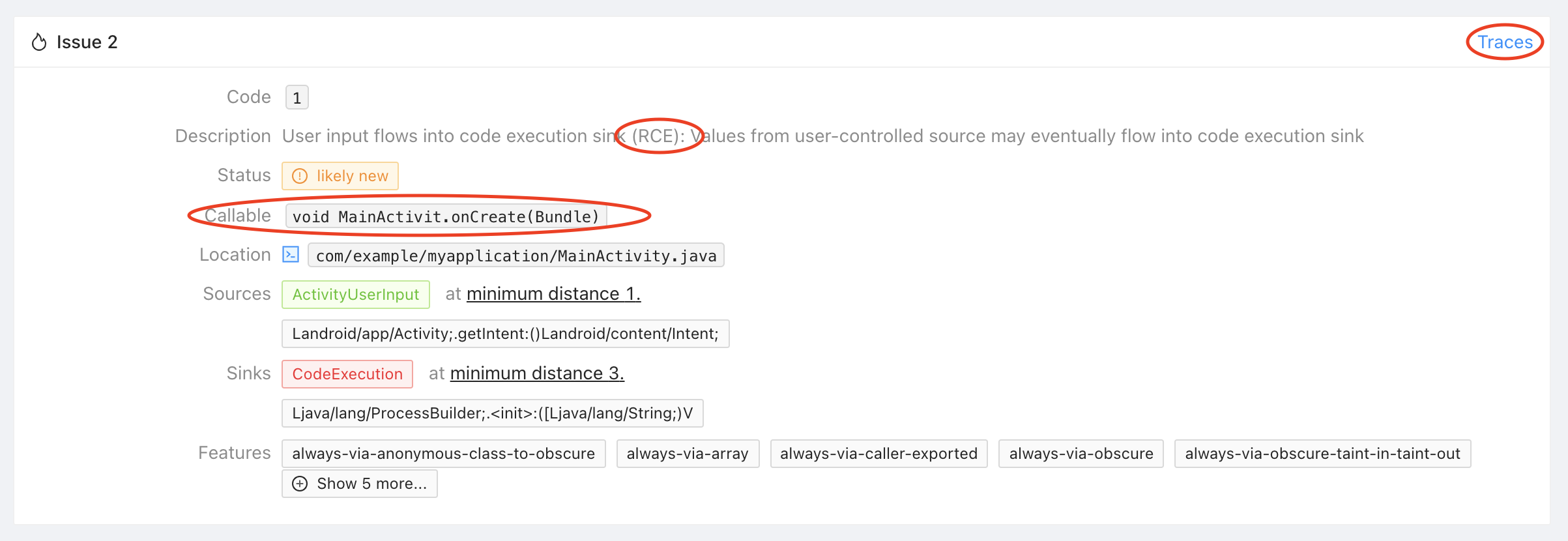
Let's focus on the remote code execution issue found in the sample app. You can identify it by its issue code 1 (for all remote code executions) and the callable void MainActivity.onCreate(Bundle). With only 4 issues to see it's easy to identify the issue manually but once more rules run, the filter functionality at the top right of the page comes in handy.
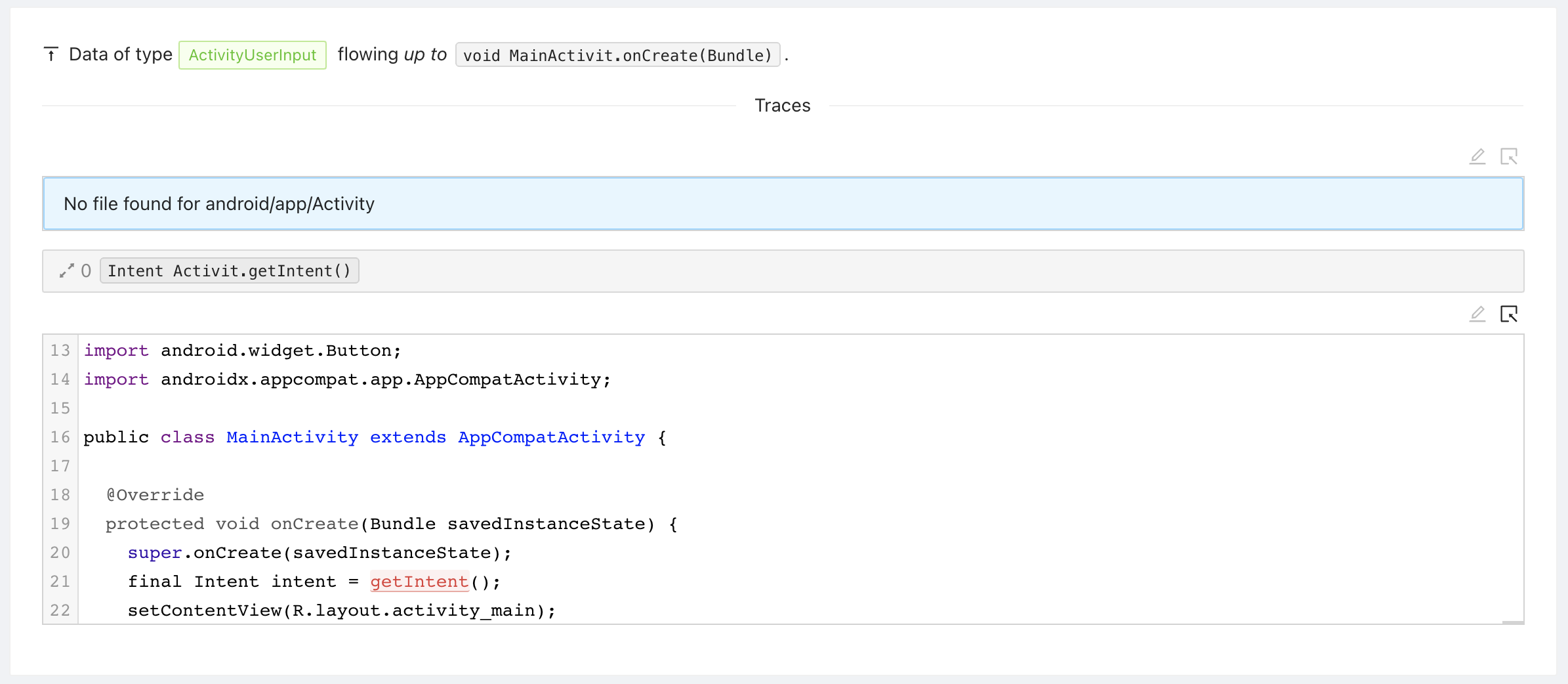
The issue tells you that Mariana Trench found a remote code execution in MainActivity.onCreate where the data is coming from Activity.getIntent one call away, and flows into the constructor of ProcessBuilder 3 calls away. Click on "Traces" in the top right corner of the issue to see an example trace.
The trace surfaced by Mariana Trench consists of three parts.
The source trace represents where the data is coming from. In our example, the trace is very short: Activity.getIntent is called in MainActivity.onCreate directly.
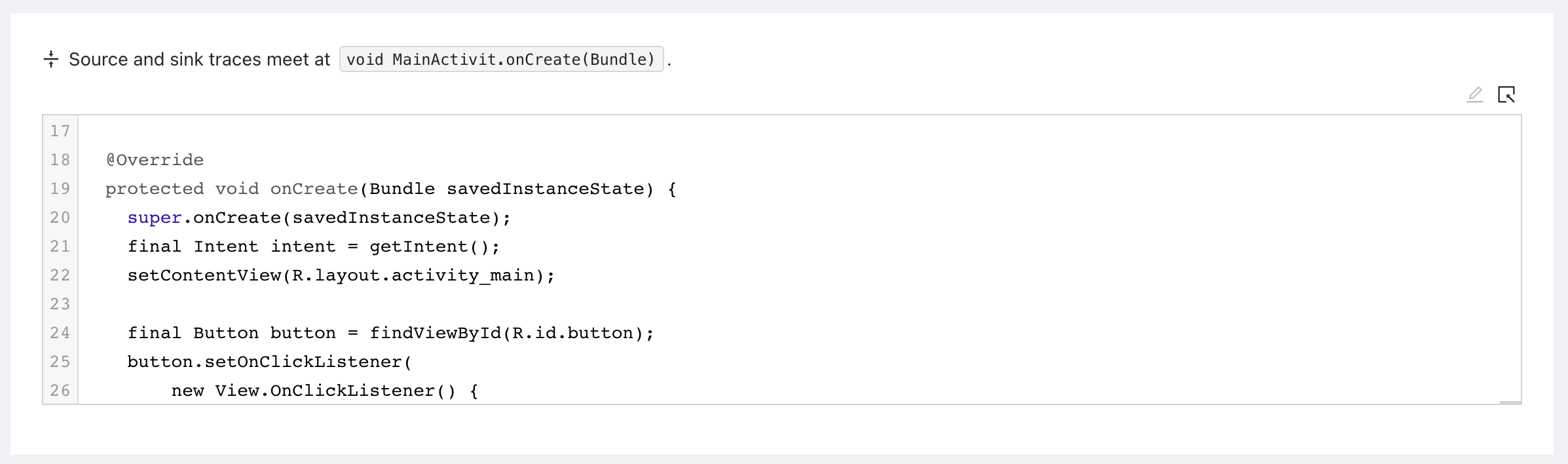
The trace root represents where the source trace meets the sink trace. In our example this is the activitie's onCreate method.
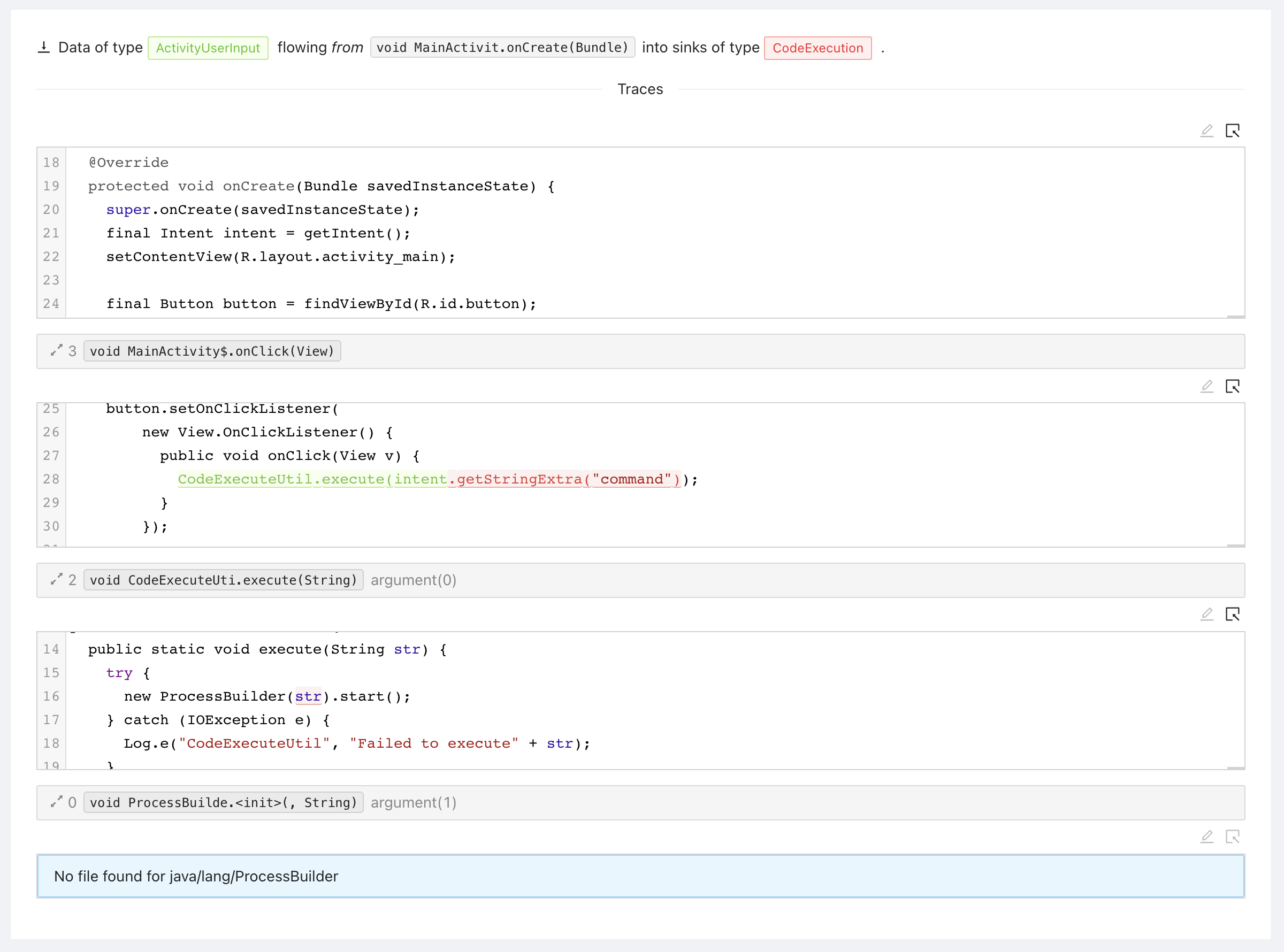
The final part of the trace is the sink trace: This is where the data from the source flows down into a sink. In our example from onCreate, to onClick, to execute, and finally into the constructor of ProcessBuilder.
Configuring Mariana Trench
You might be asking yourself, "how does the tool know what is user controlled data, and what is a sink?". This guide is meant to quickly get you started on a small app. We did not cover how to configure Mariana Trench. You can read more about that at our website under Configuration.
Contributing
For an in-depth guide on building from source and development on Mariana Trench, see the Developer's Guide at our website.
License
Mariana Trench is licensed under the MIT license.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distributions
File details
Details for the file mariana-trench-1.0.3.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: mariana-trench-1.0.3.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 4.6 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.2 CPython/3.8.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 6483ee666f0f4cfe39e32bdbf8a0b24e199d99dcb21321d821db244c7319190c |
|
| MD5 | b6c304205c87ca5ed1d2389a74d1745d |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 8fc2006489a0364352ab8e5ffea6763892aa9e51e9e0c4558f2b2850f90343ac |
File details
Details for the file mariana_trench-1.0.3-py3-none-manylinux1_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: mariana_trench-1.0.3-py3-none-manylinux1_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.3 MB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.2 CPython/3.10.6
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 927aa979a6c81c2a091496248c29e1afda1f8695ec33bd104aeaf4c5285442f3 |
|
| MD5 | 2136aa6a51f6e2e868a29c3674378282 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 9af6dc87a69adc6f84c07aa468bf1982820c04178d76607f97018889edce83b1 |
File details
Details for the file mariana_trench-1.0.3-py3-none-macosx_10_11_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: mariana_trench-1.0.3-py3-none-macosx_10_11_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 4.6 MB
- Tags: Python 3, macOS 10.11+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.2 CPython/3.8.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 1452a6d484c24f191f269fa5c27e56355e19008c333cdb8c6b4635612725070a |
|
| MD5 | f4271fb64a2675a5649b4792d0ba967a |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | f29bf3290d9978a44ccce43247c586765868df057fc80f12b9e677ac664426d7 |