Zero Noise Extrapolation (ZNE) prototype for error mitigation on
Project description
Zero Noise Extrapolation (ZNE)
Table of contents
- About This Project
- About Prototypes
- Deprecation Policy
- Using Quantum Services
- Acknowledgements
- References
- License
For users
For developers
About This Project
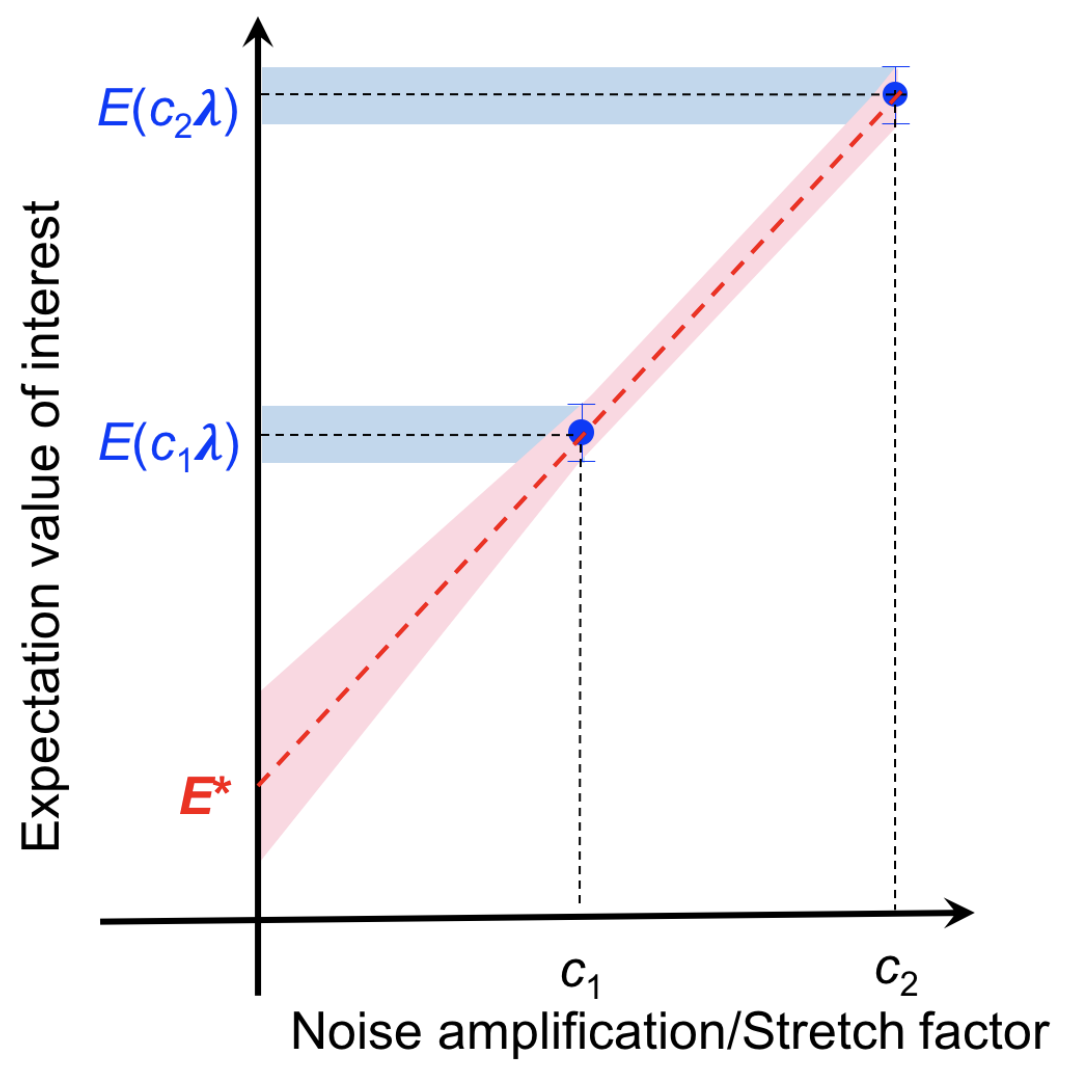
This module builds on top of the Estimator primitive official specification, providing a highly customizable zero noise extrapolation (ZNE) workflow for error mitigation on expectation value calculations. This is achieved by injecting orchestrated ZNE capabilities into an Estimator class of choice in two phases:
- Amplifying the noise introduced by the gates of input circuits.
- Extrapolating the returned expectation values to the zero noise limit.
In principle, this prototype is compatible with any Estimator class as long as it implements the qiskit.primitives.BaseEstimator interface (e.g. qiskit.primitives.Estimator, qiskit.primitives.BackendEstimator, qiskit_ibm_runtime.Estimator). Notice, however, that error mitigation techniques only make sense in the context of noisy computations; therefore using ZNE on noisless platforms (e.g. simulators), although technically possible, will not produce better results.
Furthermore, the software architecture has been devised specifically to allow users to create their custom noise amplification and extrapolation techniques, and to plug them into the overall ZNE workflow seamlessly. Libraries of pre-implemented strategies for both of these tasks are provided in the module, and external packages can easily be made to work with this tool by providing implementations of well defined interfaces for these tasks.
Before using the module for new work, users should read through the reference guide, specifically the current limitations of the module. Demo tutorials are also available as jupyter notebooks.
About Prototypes
Prototypes is a collaboration between developers and researchers that will give users early access to solutions from cutting-edge research in areas like error mitigation, quantum simulation, and machine learning. These software packages are built on top of, and may eventually be integrated into the Qiskit SDK. They are a contribution as part of the Qiskit community.
Check out our landing page and blog post for more information!
Deprecation Policy
Prototypes are meant to evolve rapidly and, as such, do not follow Qiskit's deprecation policy. We may occasionally make breaking changes in order to improve the user experience. When possible, we will keep old interfaces and mark them as deprecated, as long as they can co-exist with the new ones. Each substantial improvement, breaking change, or deprecation will be documented in CHANGELOG.md.
Using Quantum Services
If you are interested in using quantum services (i.e. using a real quantum computer, not a simulator) you can look at the Qiskit Partners program for partner organizations that have provider packages available for their offerings.
Importantly, Qiskit IBM Runtime is a quantum computing service and programming model that allows users to optimize workloads and efficiently execute them on quantum systems at scale; extending the existing interface in Qiskit with a set of new primitive programs.
Acknowledgements
- Mario Motta: for scientific insight and guidance.
- Julien Gacon: for providing a util function that maps gate names to the corresponding gate classes and for general discussions.
References
[1] Kandala, Abhinav, et al. "Extending the computational reach of a noisy superconducting quantum processor."arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.04492(2018).
[2] Stamatopoulos, Nikitas, et al. "Option pricing using quantum computers."Quantum4 (2020): 291.
[3] LaRose, Ryan, et al. "Mitiq: A software package for error mitigation on noisy quantum computers."arXiv preprintarXiv:2009.04417(2020).
[4] Kim, Youngseok, et al. "Scalable error mitigation for noisy quantum circuits produces competitive expectation values."arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.09197(2021).
License
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
File details
Details for the file prototype-zne-1.0.0rc0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: prototype-zne-1.0.0rc0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.5 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: python-requests/2.22.0
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | f834aee537a74367997f404ce9d51ca1a3834f6c9063bd63f2fb18609b25cb99 |
|
| MD5 | 7c394b90d0aaf9d7a56293a6ec6162ae |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 3fa52a6aa5fe2a4c31dc2d4bbf22ef1227ca5aa76da9dc58378dce9270df112e |
File details
Details for the file prototype_zne-1.0.0rc0-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: prototype_zne-1.0.0rc0-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 45.2 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: python-requests/2.22.0
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | aa435b86ed1f2f4ba93823f7201d1bf21b4e7be2a655d2a845582c7df4ec2980 |
|
| MD5 | cea857e950345af4cd0ddaf271896d69 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 5ffff63a4c97cea1d94921185a30f95a75dcc7e531229eb1ad014a2b37896c65 |