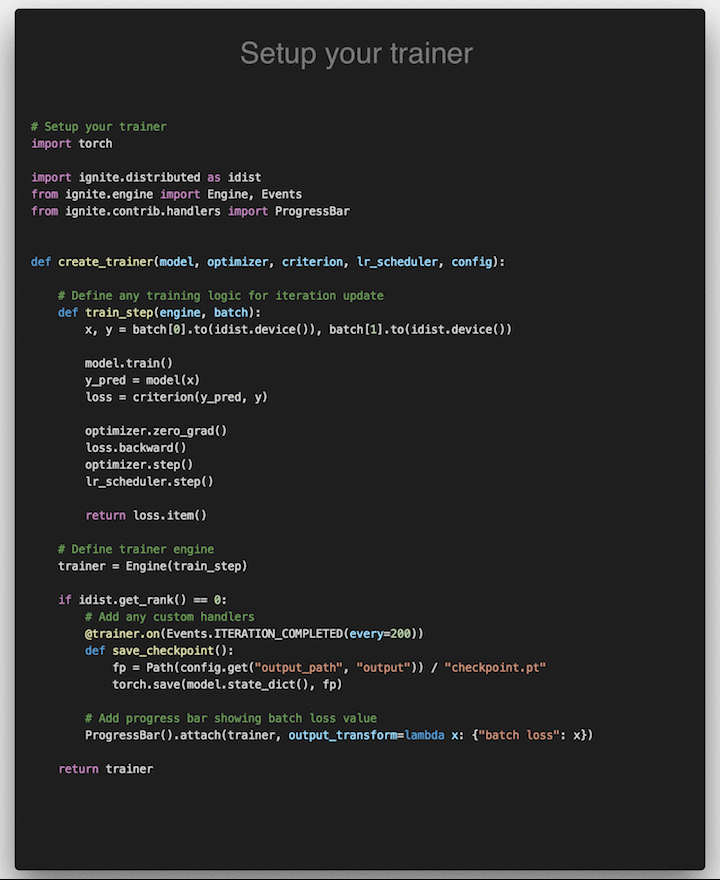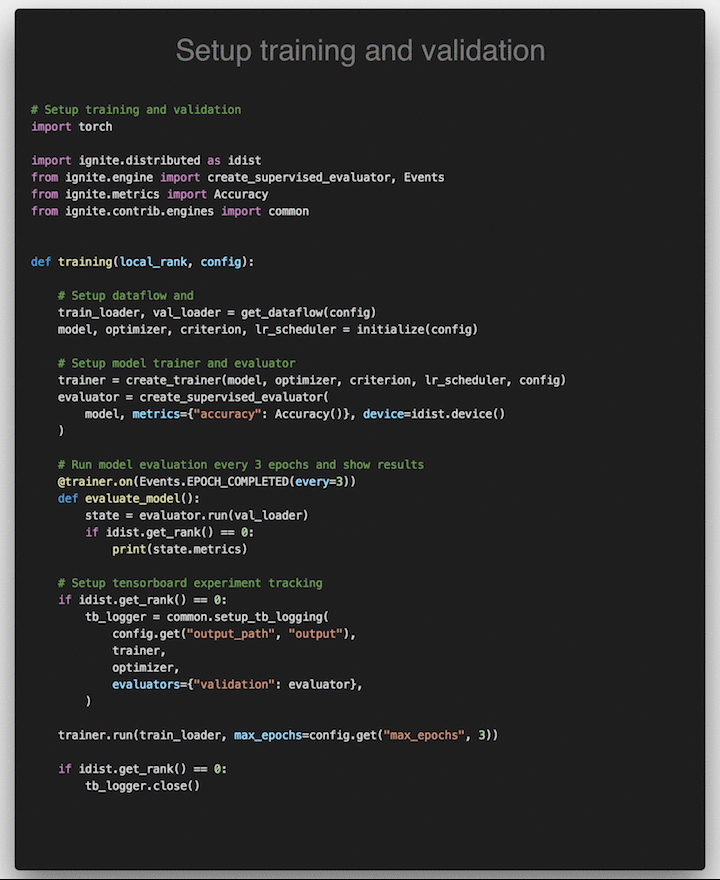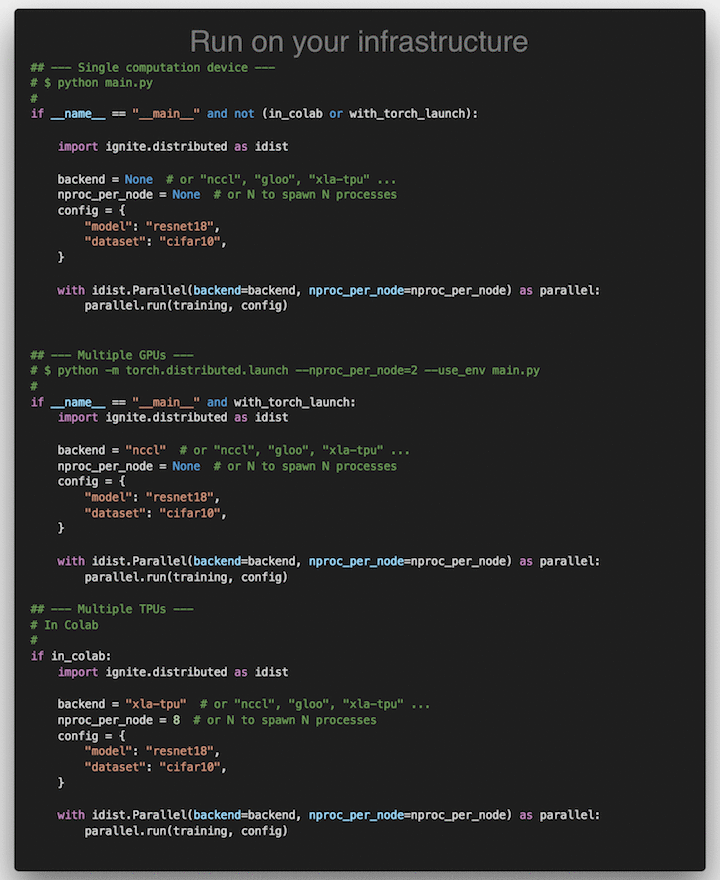
A lightweight library to help with training neural networks in PyTorch.
Project description
TL;DR
Ignite is a high-level library to help with training and evaluating neural networks in PyTorch flexibly and transparently.
Features
-
Less code than pure PyTorch while ensuring maximum control and simplicity
-
Library approach and no program's control inversion - Use ignite where and when you need
-
Extensible API for metrics, experiment managers, and other components
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- Why Ignite?
- Installation
- Getting Started
- Documentation
- Examples
- Communication
- Contributing
- Projects using Ignite
- About the team & Disclaimer
Why Ignite?
Ignite is a library that provides three high-level features:
- Extremely simple engine and event system
- Out-of-the-box metrics to easily evaluate models
- Built-in handlers to compose training pipeline, save artifacts and log parameters and metrics
Simplified training and validation loop
No more coding for/while loops on epochs and iterations. Users instantiate engines and run them.
Example
from ignite.engine import Engine, Events, create_supervised_evaluator
from ignite.metrics import Accuracy
# Setup training engine:
def train_step(engine, batch):
# Users can do whatever they need on a single iteration
# E.g. forward/backward pass for any number of models, optimizers etc
# ...
trainer = Engine(train_step)
# Setup single model evaluation engine
evaluator = create_supervised_evaluator(model, metrics={"accuracy": Accuracy()})
def validation():
state = evaluator.run(validation_data_loader)
# print computed metrics
print(trainer.state.epoch, state.metrics)
# Run model's validation at the end of each epoch
trainer.add_event_handler(Events.EPOCH_COMPLETED, validation)
# Start the training
trainer.run(training_data_loader, max_epochs=100)
Power of Events & Handlers
The cool thing with handlers is that they offer unparalleled flexibility (compared to say, callbacks). Handlers can be any function: e.g. lambda, simple function, class method etc. Thus, we do not require to inherit from an interface and override its abstract methods which could unnecessarily bulk up your code and its complexity.
Execute any number of functions whenever you wish
Examples
trainer.add_event_handler(Events.STARTED, lambda _: print("Start training"))
# attach handler with args, kwargs
mydata = [1, 2, 3, 4]
logger = ...
def on_training_ended(data):
print(f"Training is ended. mydata={data}")
# User can use variables from another scope
logger.info("Training is ended")
trainer.add_event_handler(Events.COMPLETED, on_training_ended, mydata)
# call any number of functions on a single event
trainer.add_event_handler(Events.COMPLETED, lambda engine: print(engine.state.times))
@trainer.on(Events.ITERATION_COMPLETED)
def log_something(engine):
print(engine.state.output)
Built-in events filtering
Examples
# run the validation every 5 epochs
@trainer.on(Events.EPOCH_COMPLETED(every=5))
def run_validation():
# run validation
# change some training variable once on 20th epoch
@trainer.on(Events.EPOCH_STARTED(once=20))
def change_training_variable():
# ...
# Trigger handler with customly defined frequency
@trainer.on(Events.ITERATION_COMPLETED(event_filter=first_x_iters))
def log_gradients():
# ...
Stack events to share some actions
Examples
Events can be stacked together to enable multiple calls:
@trainer.on(Events.COMPLETED | Events.EPOCH_COMPLETED(every=10))
def run_validation():
# ...
Custom events to go beyond standard events
Examples
Custom events related to backward and optimizer step calls:
from ignite.engine import EventEnum
class BackpropEvents(EventEnum):
BACKWARD_STARTED = 'backward_started'
BACKWARD_COMPLETED = 'backward_completed'
OPTIM_STEP_COMPLETED = 'optim_step_completed'
def update(engine, batch):
# ...
loss = criterion(y_pred, y)
engine.fire_event(BackpropEvents.BACKWARD_STARTED)
loss.backward()
engine.fire_event(BackpropEvents.BACKWARD_COMPLETED)
optimizer.step()
engine.fire_event(BackpropEvents.OPTIM_STEP_COMPLETED)
# ...
trainer = Engine(update)
trainer.register_events(*BackpropEvents)
@trainer.on(BackpropEvents.BACKWARD_STARTED)
def function_before_backprop(engine):
# ...
- Complete snippet can be found here.
- Another use-case of custom events: trainer for Truncated Backprop Through Time.
Out-of-the-box metrics
-
Metrics for various tasks: Precision, Recall, Accuracy, Confusion Matrix, IoU etc, ~20 regression metrics.
-
Users can also compose their own metrics with ease from existing ones using arithmetic operations or torch methods.
Example
precision = Precision(average=False)
recall = Recall(average=False)
F1_per_class = (precision * recall * 2 / (precision + recall))
F1_mean = F1_per_class.mean() # torch mean method
F1_mean.attach(engine, "F1")
Installation
From pip:
pip install pytorch-ignite
From conda:
conda install ignite -c pytorch
From source:
pip install git+https://github.com/pytorch/ignite
Nightly releases
From pip:
pip install --pre pytorch-ignite
From conda (this suggests to install pytorch nightly release instead of stable version as dependency):
conda install ignite -c pytorch-nightly
Docker Images
Using pre-built images
Pull a pre-built docker image from our Docker Hub and run it with docker v19.03+.
docker run --gpus all -it -v $PWD:/workspace/project --network=host --shm-size 16G pytorchignite/base:latest /bin/bash
List of available pre-built images
Base
pytorchignite/base:latestpytorchignite/apex:latestpytorchignite/hvd-base:latestpytorchignite/hvd-apex:latestpytorchignite/msdp-apex:latest
Vision:
pytorchignite/vision:latestpytorchignite/hvd-vision:latestpytorchignite/apex-vision:latestpytorchignite/hvd-apex-vision:latestpytorchignite/msdp-apex-vision:latest
NLP:
pytorchignite/nlp:latestpytorchignite/hvd-nlp:latestpytorchignite/apex-nlp:latestpytorchignite/hvd-apex-nlp:latestpytorchignite/msdp-apex-nlp:latest
For more details, see here.
Getting Started
Few pointers to get you started:
- Quick Start Guide: Essentials of getting a project up and running
- Concepts of the library: Engine, Events & Handlers, State, Metrics
- Full-featured template examples (coming soon ...)
Documentation
- Stable API documentation and an overview of the library: https://pytorch.org/ignite/
- Development version API documentation: https://pytorch.org/ignite/master/
- FAQ, "Questions on Github" and "Questions on Discuss.PyTorch".
- Project's Roadmap
Additional Materials
- PyTorch Ecosystem Day 2021 Breakout session presentation
- Tutorial blog post about PyTorch-Ignite
- 8 Creators and Core Contributors Talk About Their Model Training Libraries From PyTorch Ecosystem
- Ignite Posters from Pytorch Developer Conferences:
Examples
Tutorials
Text Classification using Convolutional Neural Networks
Variational Auto Encoders
Convolutional Neural Networks for Classifying Fashion-MNIST Dataset
Training Cycle-GAN on Horses to Zebras with Nvidia/Apex - logs on W&B
Another training Cycle-GAN on Horses to Zebras with Native Torch CUDA AMP - logs on W&B
Finetuning EfficientNet-B0 on CIFAR100
Hyperparameters tuning with Ax
Basic example of LR finder on MNIST
Benchmark mixed precision training on Cifar100: torch.cuda.amp vs nvidia/apex
MNIST training on a single TPU
CIFAR10 Training on multiple TPUs
Basic example of handlers time profiling on MNIST training example
Reproducible Training Examples
Inspired by torchvision/references, we provide several reproducible baselines for vision tasks:
- ImageNet - logs on Ignite Trains server coming soon ...
- Pascal VOC2012 - logs on Ignite Trains server coming soon ...
Features:
- Distributed training: native or horovod and using PyTorch native AMP
Communication
-
GitHub issues: questions, bug reports, feature requests, etc.
-
Discuss.PyTorch, category "Ignite".
-
PyTorch-Ignite Discord Server: to chat with the community
-
GitHub Discussions: general library related discussions, ideas, Q&A, etc.
User feedback
We have created a form for "user feedback". We appreciate any type of feedback and this is how we would like to see our community:
- If you like the project and want to say thanks, this the right place.
- If you do not like something, please, share it with us and we can see how to improve it.
Thank you !
Contributing
Please see the contribution guidelines for more information.
As always, PRs are welcome :)
Projects using Ignite
Research papers
- BatchBALD: Efficient and Diverse Batch Acquisition for Deep Bayesian Active Learning
- A Model to Search for Synthesizable Molecules
- Localised Generative Flows
- Extracting T Cell Function and Differentiation Characteristics from the Biomedical Literature
- Variational Information Distillation for Knowledge Transfer
- XPersona: Evaluating Multilingual Personalized Chatbot
- CNN-CASS: CNN for Classification of Coronary Artery Stenosis Score in MPR Images
- Bridging Text and Video: A Universal Multimodal Transformer for Video-Audio Scene-Aware Dialog
- Adversarial Decomposition of Text Representation
- Uncertainty Estimation Using a Single Deep Deterministic Neural Network
- DeepSphere: a graph-based spherical CNN
- Norm-in-Norm Loss with Faster Convergence and Better Performance for Image Quality Assessment
- Unified Quality Assessment of In-the-Wild Videos with Mixed Datasets Training
- Deep Signature Transforms
- Neural CDEs for Long Time-Series via the Log-ODE Method
- Volumetric Grasping Network
- Mood Classification using Listening Data
- Deterministic Uncertainty Estimation (DUE)
Blog articles, tutorials, books
- State-of-the-Art Conversational AI with Transfer Learning
- Tutorial on Transfer Learning in NLP held at NAACL 2019
- Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Hands-On-Second-Edition, published by Packt
- Once Upon a Repository: How to Write Readable, Maintainable Code with PyTorch
- The Hero Rises: Build Your Own SSD
- Using Optuna to Optimize PyTorch Ignite Hyperparameters
Toolkits
Others
- Implementation of "Attention is All You Need" paper
- Implementation of DropBlock: A regularization method for convolutional networks in PyTorch
- Kaggle Kuzushiji Recognition: 2nd place solution
- Unsupervised Data Augmentation experiments in PyTorch
- Hyperparameters tuning with Optuna
- Logging with ChainerUI
- FixMatch experiments in PyTorch and Ignite (CTA dataaug policy)
- Kaggle Birdcall Identification Competition: 1st place solution
See other projects at "Used by"
If your project implements a paper, represents other use-cases not covered in our official tutorials, Kaggle competition's code or just your code presents interesting results and uses Ignite. We would like to add your project in this list, so please send a PR with brief description of the project.
About the team & Disclaimer
PyTorch-Ignite is a NumFOCUS Affiliated Project, operated and maintained by volunteers in the PyTorch community in their capacities as individuals (and not as representatives of their employers). See the "About us" page for a list of core contributors. For usage questions and issues, please see the various channels here. For all other questions and inquiries, please send an email to contact@pytorch-ignite.ai.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distributions
File details
Details for the file pytorch-ignite-0.5.0.dev20210423.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: pytorch-ignite-0.5.0.dev20210423.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 157.4 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.4.1 importlib_metadata/4.0.1 pkginfo/1.7.0 requests/2.25.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.60.0 CPython/3.8.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | ccfe564ec129bdc290f166153e7d257ef30b4d5c7b7db2f00a24de7252309422 |
|
| MD5 | c0a808bb7c46117d9b4e9fd31599ba58 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 43970c79fd6689c3c2b4868653ad2f559a9176e19ff855352f54de74914780fd |
File details
Details for the file pytorch_ignite-0.5.0.dev20210423-py3.8.egg.
File metadata
- Download URL: pytorch_ignite-0.5.0.dev20210423-py3.8.egg
- Upload date:
- Size: 507.3 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.4.1 importlib_metadata/4.0.1 pkginfo/1.7.0 requests/2.25.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.60.0 CPython/3.8.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 0784495db9b36576cc3e1e8f0ac030c9bfcd6c804e6965cfb8556a134c645f8c |
|
| MD5 | 1f93b146cb1449d18f2a18c2b922b2ca |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | b7b2482060ba46926d2f27c6c6c41437be6a55657da479781fd81f6ad819c18f |
File details
Details for the file pytorch_ignite-0.5.0.dev20210423-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: pytorch_ignite-0.5.0.dev20210423-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 214.9 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.4.1 importlib_metadata/4.0.1 pkginfo/1.7.0 requests/2.25.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.60.0 CPython/3.8.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 16a5f670187b54d47d3957f18e28a40fd862105d213d3f521e6c8cfce23e099b |
|
| MD5 | daa437c6981463b3d129a444ed569b31 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | dd0ec669dd04c92cbd194257405d65ec0e38407e1e953d52ec8f73ea35c6a068 |